2764
Views & Citations1764
Likes & Shares
Objective: To compare a case of thoracic myelopathy secondary to degenerative thoracic spondylolisthesis with previously reported cases and radiologically assess the cause of degenerative thoracic spondylolisthesis.
Summary and background data: The thoracic and costovertebral joints provide relative stability to the upper and middle thoracic spine. Therefore, thoracic myelopathy of the lower thoracic spine associated with degenerative thoracic spondylolisthesis is rare. We report a case of degenerative spondylolisthesis of T11 associated with thoracic myelopathy.
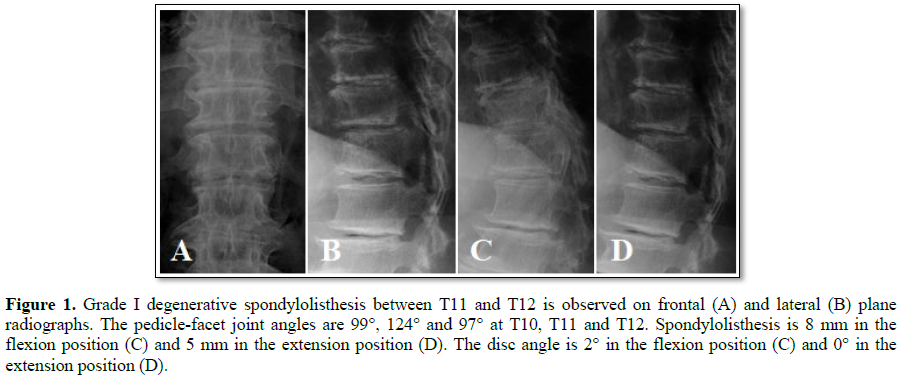
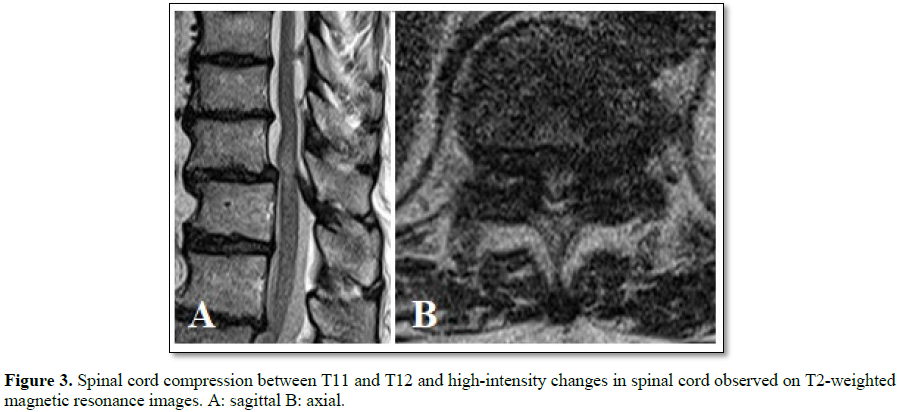
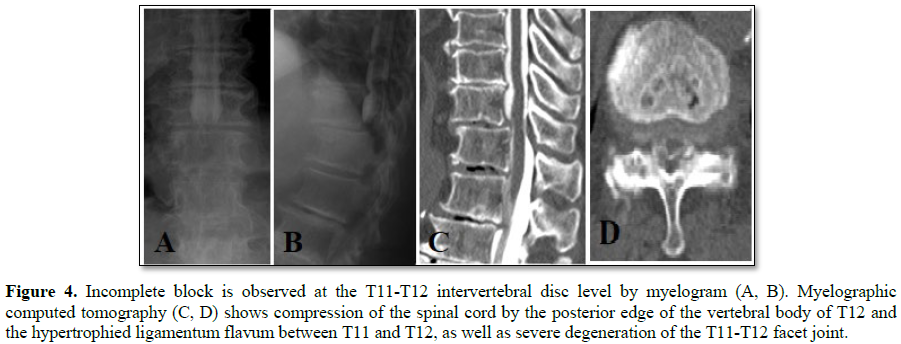
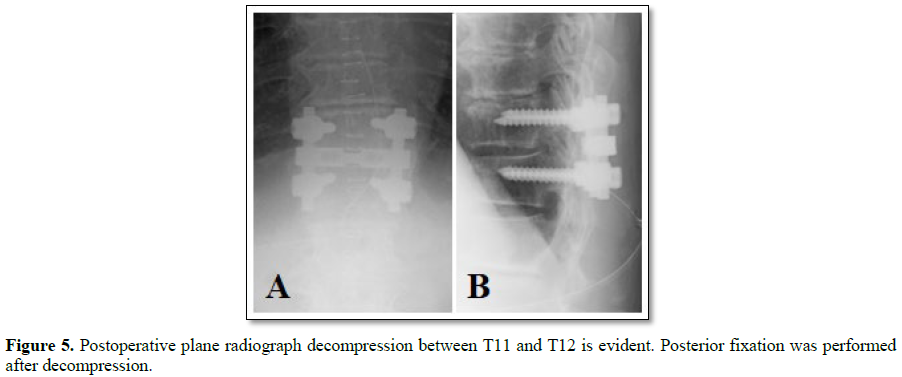
Methods: A 76 year old woman with numbness in both lower limbs and gait disturbance was diagnosed with grade I degenerative spondylolisthesis of T11 on plain radiography according to the Meyerding classification. Stenosis of the spinal canal at T11-T12 and signal changes in the spinal cord were observed on sagittal T2-weighted MR images. Myelography identified an incomplete block at T11-T12 and computed tomography images showed severe facet joint degeneration between T11 and T12. A posterior decompression was performed combined with fixation of T11 and T12.
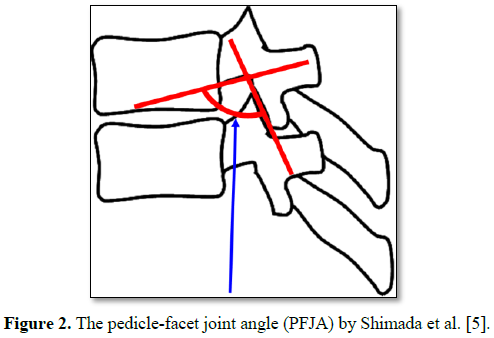
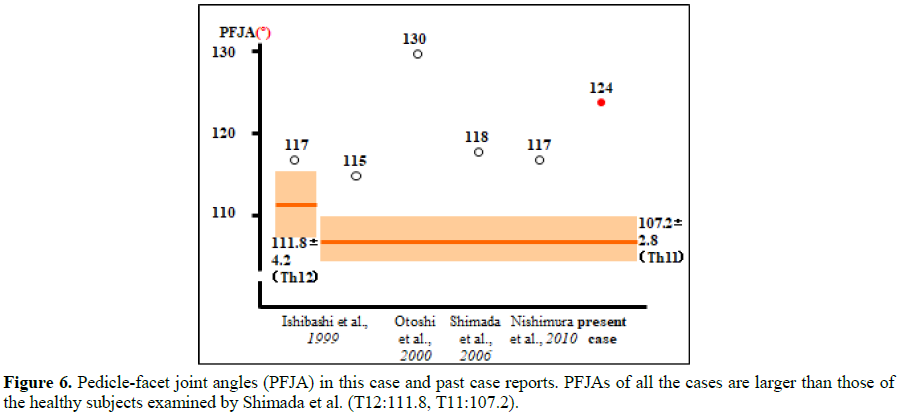
Results: The pedicle-facet joint angle at T11 was 124°, which was larger than that at T10 (99°) and T12 (97°).
INTRODUCTION
The thoracic and facet joints provide flexion-extension stability to the upper and middle thoracic spine. However, very few cases of thoracic myelopathy in the thoracolumbar area (lower thoracic spine level) due to spondylolisthesis have been reported. We report a patient with degenerative spondylolisthesis of T11 who presented with thoracic myelopathy.
CASE REPORT
History and clinical examination
SURGICAL PROCEDURE
Postoperatively there was an improvement in the spasticity of the lower limbs and poor gait, but the numbness persisted. The patient was able to walk using a wheeled walker at a follow-up examination after 2 years.
DISCUSSION
The thoracic and costovertebral joints provide support and stability to the upper and middle thoracic spine, relative to the lumbar spine. However, similar structures do not exist in the thoracolumbar area, thus greater mobility often causes spondylosis [3]. A paper by Aizawa et al. [4] revealed that thoracic myelopathy affects mostly the lower thoracic spine, especially at Th11/12 and that 52% of these cases are associated with ossification of the ligamentum flavum, especially in Asian patients while only 8% are associated with thoracic spondylosis. Thoracic spondylolisthesis is rare, especially degenerative spondylolisthesis, because the facet joints are parallel to the coronal plane at the thoracic level. Extensive search of the PubMed 1990-2013 library and the Japan Medical Abstracts Society (JAMAS) showed 5 only such cases [1,2,5,6]. Ishibashi et al. [1] suggested that intervertebral slippage presents with large arch angles. In the present case, the PFJA between T11 and T12 was 124°, which indicated leveling of the T11 facet joint.
CONCLUSION
· A rare case of myelopathy secondary to thoracic spondylolisthesis was experienced.
· We performed posterior decompression with fixation for this case.
1. Ishibashi K, Ishii Y, Yamazaki S (1999) Thoracic myelopathy due to degenerative spondylolisthesis in the lower thoracic spine: A report of two cases. Orthop Surg Traumatol 42: 1369-1373 (in Japanese).
2. Otoshi K, Watanabe E, Watanabe T (2000) A case of degenerative thoracic spondylolisthesis. Tohoku Seisai Kiyo 44: 25-28 (in Japanese).
3. Sato T, Kokubun S, Tanaka Y (1998) Thoracic myelopathy in the Japanese: Epidemiological and clinical observations on the cases in Miyagi prefecture. Tohoku J Exp Med 184: 1-11.
4. Aizawa T, Sato T, Tanaka Y (2006) Thoracic myelopathy in Japan: Epidemiological retrospective study in Miyagi prefecture during 15 years. Tohoku J Exp Med 210: 199-208.
5. Shimada Y, Kasukawa Y, Miyakoshi N (2006) Spondylolisthesis of the thoracic spine. J Neurosurg Spine 4: 415-418.
6. Nishimura S, Ishikawa M, Fujita N (2010) Spondylolisthesis of the thoracic spine with Scheuermann’s disease. Case report. Rinsho Seikei Geka 45: 1153-1157 (in Japanese).
QUICK LINKS
- SUBMIT MANUSCRIPT
- RECOMMEND THE JOURNAL
-
SUBSCRIBE FOR ALERTS
RELATED JOURNALS
- International Journal of Surgery and Invasive Procedures (ISSN:2640-0820)
- Journal of Clinical Trials and Research (ISSN:2637-7373)
- Ophthalmology Clinics and Research (ISSN:2638-115X)
- Oncology Clinics and Research (ISSN: 2643-055X)
- Journal of Renal Transplantation Science (ISSN:2640-0847)
- International Journal of Clinical Case Studies and Reports (ISSN:2641-5771)
- Journal of Alcoholism Clinical Research