4610
Views & Citations3610
Likes & Shares
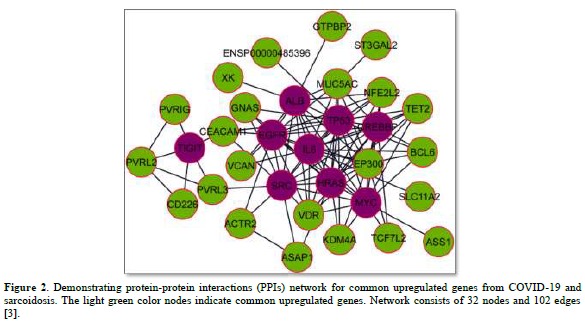
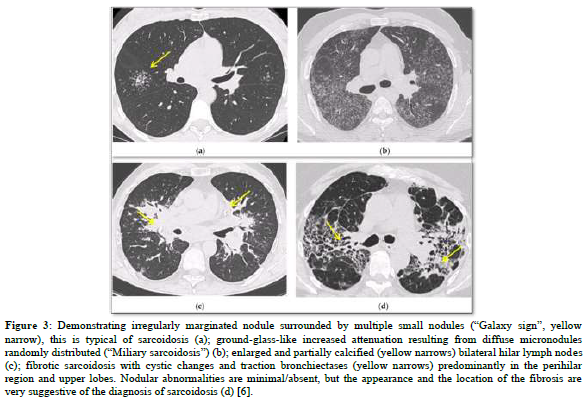
Several post-COVID-19 inflammatory disorders and autoimmune diseases have been discovered [1] since global COVID-19 pandemic started [2]. Association between these diseases is still to be investigated [2]. Common genes between COVID-19 and sarcoidosis are demonstrated in Figures 1 & 2 [3]. Nevertheless, sarcoidosis organ involvement, demographics, and type of sarcoidosis treatment at the time of COVID-19 diagnosis are related to hospital admission, non-invasive ventilation or high flow oxygenation, intubation [4]. A retrospective hospital-based cohort study of 585 French sarcoidosis patients in 2017, demonstrated an estimate of a 5 % frequency of severe infections that resulting in hospital admission and death [5]. A typical HRCT feature in sarcoidosis is the presence of well-defined micronodules scattered along the broncho-vascular bundle, veins, fissures and pleura in a characteristic lymphatic distribution. Occasionally, “galaxy sign”, a highly suggestive of pulmonary sarcoidosis (predominance of a mid-to-upper lung zones) may demonstrates conglomerate masses that are surrounded by a multitude of micronodules (Figure 3) [6].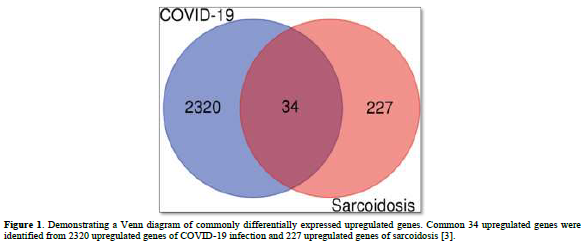
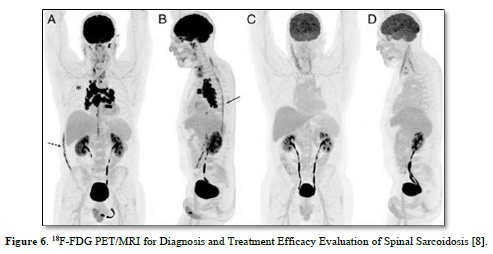
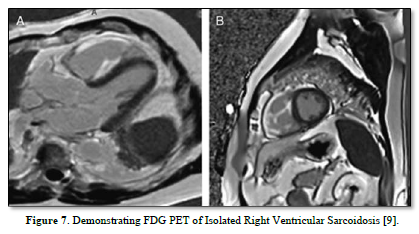
Besides sarcoidosis of lungs, symptomatic and accidental extrapulmonary sarcoidosis is also found around the world (Figures 5-7) [7-9].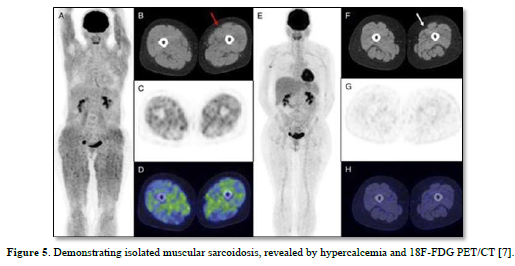
In conclusion, hub gene identification might have significant roles in modulating sarcoidosis and COVID-19 infection. In the literature, cases with sarcoid-like granuloma have been reported very few. Sarcoid-like immune response to COVID-19 could be noncaseating granulomas due to short time from disease to develop granuloma.
- Galeotti C, Baryl J (2020) Autoimmune and inflammatory diseases following COVID-19. Nat Rev Rheumatol 16(8): 413-414.
- Racil H, Znegui T, Maazoui S, Touil A, Habibech S, Henda N, et al. (2023) Can coronavirus disease 2019 induce sarcoidosis: A case report. Thorac Res Pract 24(1): 45-48.
- Mogal R, Sovupa SA, Junayed A, Mahmod R, Abedin Z, Sikder S (2022) Common genetic aspects between COVID-19 and sarcoidosis: A network-based approach using expression data. Biochem Biophys Rep 29: 101219.
- Nadeem O, Sharma A, Alaouie D, Bradley P, Ouellette D (2021) Outcome in patients with sarcoidosis diagnosed with COVID-19. Presentation at Chest 2021 Annual Meeting, pp: 17-20.
- Dureault A, Chapelon C, Biard L, Domont F, Savey L, et al. (2017) Severe infections in sarcoidosis: Incidence, predictors and long-term outcome in a cohort of 585 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 96: e8846.
- Bernardinello N, Petrarulo S, Balestro E, Cocconcelli E, Veltkamp M, Spagnolo P (2021) Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis. Diagnostics (Basel) 11(9):1558.
- Dhomps A, Thibault F, Streichenberger N, Andrea S, Jeremie T (2019) Isolated muscular sarcoidosis revealed by hypercalcemia. Clin Nucl Med 44(10): 824-825.
- Ashjan K, Darejan B, Lea F, Mathilde H, Vincent P, Imperiale, et al. (2024) 18F-FDG PET/MRI for diagnosis and treatment efficacy evaluation of spinal sarcoidosis. Clin Nucl Med 49(1): e28-e30.
- Alan S, Dagmar HS (2023) FDG PET of Isolated Right Ventricular Sarcoidosis. Clin Nucl Med 48(2): 184-185.
QUICK LINKS
- SUBMIT MANUSCRIPT
- RECOMMEND THE JOURNAL
-
SUBSCRIBE FOR ALERTS
RELATED JOURNALS
- Archive of Obstetrics Gynecology and Reproductive Medicine (ISSN:2640-2297)
- International Journal of Internal Medicine and Geriatrics (ISSN: 2689-7687)
- Journal of Cancer Science and Treatment (ISSN:2641-7472)
- Journal of Allergy Research (ISSN:2642-326X)
- Advance Research on Alzheimers and Parkinsons Disease
- Journal of Ageing and Restorative Medicine (ISSN:2637-7403)
- Journal of Oral Health and Dentistry (ISSN: 2638-499X)









