7050
Views & Citations6050
Likes & Shares
Keyword: Leadership, Performance, Reward, Situational
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
The way in which a company efficiently manages, influences as well as improve the efficiency of employees is needed for the accomplishment of the organizational goals, as for many organizations lack the effective leaders, putting them in a position of missing the necessary occurrence in building their capacities, making it inappropriate practices in leadership style. Poor performance can result from unfulfilled external or internal factors, work stress is caused by lack of resources and equipment; work schedules such as working late or overtime and organizational climate are considered as contributors to employees’ stress, work stress often shows high dissatisfaction among the employees, job mobility, burnout, poor work performance and less effective interpersonal relations at work (Chong, 2010). It was observed that role ambiguity has its own drawbacks. In the work environment wherever is role ambiguity, negative vibes of employees as lack of self-conviction and disappointment drives human resource’s hope towards misery and despair. Poor reward system has been a major factor affecting employees’ productivity, commitment and satisfaction. The lack of information on relationship between situational leadership, reward and employee performance creates a gap in knowledge on how situational leadership, reward increasingly affected employees, performance in banking, public sector especially in the African and particularly in Nigeria context. Against this backdrop this study seeks to investigates situational leadership reward and employee performance in in the Nigerian banking industry. Based on the above challenges, the study was guided by four research questions, objectives and hypotheses.
- To what extend does directive dimension of situational leadership have effect on employee performance among commercial banks?
- To what extend does effect of supportive dimension of situational leadership have effect on employee performance among commercial banks?
- What is the effect of extrinsic dimension reward system on employee performance at among commercial banks?
- What is the effect of intrinsic dimension reward system on employee performance at among commercial banks?
Objectives of the study
- To examine the effects of directive dimension of situational leadership have on employee performance among commercial banks.
- To examine the effects of supportive dimension of situational leadership on employee performance among commercial banks.
- To ascertain the effect of extrinsic dimension reward system on employee performance among commercial banks.
- To examine effect of intrinsic dimension reward system on employee performance among commercial banks.
Research hypotheses
- Ho1: Directive dimension of situational leadership does not have a significant effect on employee performance among commercial banks.
- Ho2: Supportive dimension of situational leadership does not have a significant effect on employee performance among commercial banks.
- Ho3: Extrinsic dimension of reward system does not have a significant effect on employee performance among commercial banks.
- Ho4: Intrinsic dimension of reward system does not have a significant effect on employee performance among commercial banks.
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE STUDY
Theoretical significance
To the scholars, the findings of this study will add value to the current body of knowledge as it recommends ways for enhancement of employee’s performance through situational leadership reward.
Practical significance
The findings of this study will support leaders in all sectors especially in evaluating the importance of leadership styles with situational leadership reward on employee’s performance in aspect of motivation.
Policy significance
The findings of this study will also be supportive to the policy makers because it will shed more light on situational leadership in order to assist them in formulating a better policy for the organization.
Scope of the study
The study is limited to situational leadership (directive awareness, supportive vision, coaching responsibility and delegating action) reward, and employee performance in deposit money bank. The study covered commercial banks in Jos North local government area of plateau state. The unit of analysis will be the employees of those selected banks in Jos North LGA of plateau state. The study is expected to cover the period of five (5) years, and durations for 2 years.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Conceptual Review
This segment will review relevant literatures on the constructs- situational leadership dimensions and employees’ performance in order to give a better understanding of the framework depicted below.
Employee performance
The main goal of any organization is to enhance the job performance of its employees so that it could survive in this highly competitive environment. Performance is a multidimensional construct and an extremely vital criterion that determines organizational successes or failures. Prasetya & Kato, (2011) Refer to performance as the attained outcomes of actions with skills of employees who perform in some situation. According to Pattanayak (2005), the performance of an employee is his/her resultant behavior on a task which can be observed and evaluated. Employees need good leadership and work atmosphere to perform their best.
Employee performance and rewards
Employee reward plays a crucial role in the achievement of employee performance (Rasool, Arfeen, Mothi & Aslam, 2015). Many academic studies have identified and underscored the role of motivation in the workplace and how it supports and fosters employee performance (Ahmed and Farooqi, 2020). Although remote working is a workplace strategy initiated or agreed to by organizations, the performance of remote workers (with focus on dimensions such as their problem-solving ability, quality of work, time management, and productivity) will be dependent on many factors, one of which is the reward they get from their employers (Muhammad, 2022). Specifically, it has been argued that to derive employee commitment to set organizational goals and to improve performance in the workplace, employees will need to be motivated (Kuruzovich, Paczkowski, Golden, Goodarzi & Venkatesh, 2021; Eziokwu, & Onuaha, 2021).
Employees performance and situational leadership styles
Several scholars and studies have often discussed the correlation between leadership style and employee's performance; most of the studies show that leadership style has a significant correlation with employees' performance, although the significances may be a positive or negative correlation with employee's performance depending on the leadership style adopted by leaders of the organization (Fu-Jin, 2010). Scholars like Eziokwu, & Onuaha, 2021). posit that visionary leadership somewhat leads to cohesion, trust, commitment, motivation, and enhances performance in the organizational environment. (Smith, 2016). believe that attention should be paid on the effect of leadership when an organization wishes to seek efficient ways to be ahead of the competition. Leadership plays a vital role in reshaping collective norms, coordinating collective action, and helping team members cope with their environments.
Situational leadership
Situational leadership allows individuals to become responsive to the potential benefits of the participatory approach to decision-making while also knowing that in certain situations, they will have to make decisions on their own. Administrators need to know which factors to consider when analyzing a situation and opt for the leader decision style that best fits the problem to be resolved. Situational leadership according to Fiedler in Gibson, Ivancevich, Donnelly, Konopaske (2003) is a leader contribution toward the effectiveness of group performance depends on way or leadership style and the favorableness of the situation which it faced. Situational leadership indicators used in this research was the LPC (Least Preferred Coworker) is a way to measure whether a person is task-oriented or relationship.
Effective situational leadership
The fiedler contingency model proposes that “effective groups depend on a proper match between a leader’s style of interacting with subordinates and the degree to which the situation gives control and influence to the leader” (Kritsonis, 2004). The cognitive research theory isolates stress as a situational factor. This theory states that stress has a negative impact on a situation.
Situational leadership and performance
Situational leadership proposes that effective leadership requires a rational understanding of the situation and an appropriate response, rather than a charismatic leader with a large group of dedicated followers (Graeff, 1997; Grint, 2011). Situational leadership in general evolved from a task-oriented versus people-oriented leadership continuum (Bass, 2008; Conger et al., 2010; Graeff, 1997).
Reward
Rewards refer to all form of financial returns and tangible services and benefits an employee receives as part of an employment relationship. “reward is the benefits that arise from performing a task, rendering a service or discharging a responsibility” (Colin, cited in Waruni, 2014). Reward system according to Armstrong (2001) consists of an organization’s integrated policies, processes and practices for rewarding its employees in accordance with their contribution, skill and competence and their markets worth.
Dimensions of situational leadership
Supporting: Gumusluoglu & Ilsev, (2009) said that innovation and using the allocated adequate resources for innovation properly support the internal climate which is an essential factor that plays an important role in the relationship.
Delegating: Schriesheim, (1998) found that leaders prefer to delegate tasks to individuals who are trusted. Klein, et al. (2006) stated that delegation allows beginners to practice and grow into leaders, thus improving the performance. Harold & Holtz, (2015) said that delegating will motivate subordinates to do more than expected, delegating as the leader depends on the team and gives them the authority and responsibilities for performing and doing the tasks, leader withdraws from regular support minimize his control and encourage team results, empower team decision making “low directing, low supporting”.
How leadership influences performance within an organization
The resource-based view of the firm identifies strategic human resource management as a means of gaining competitive advantage through people. Resources confer lasting competitive advantage on a firm to the extent that they remain hard to duplicate, have no direct substitutes and enable organizations to pursue opportunities (Richard, 2000).
Conceptual model
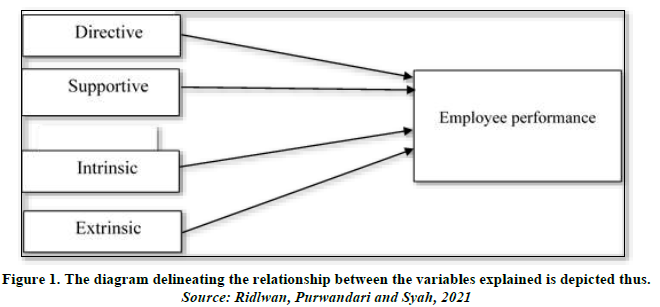
The research framework depicts that the dimensions of situational leadership (directive and supportive) and reward (intrinsic and extrinsic), has direct linear relationship with employee performance, which depicts the research questions, objectives and hypothesis. It entails the influence of the dimensions of independent variables (directive and supportive) and (intrinsic and extrinsic) on dependent variable employee performance.
Conceptual framework
The diagram delineating the relationships between the variables explained is depicted thus: (Figure 1).
Theoretical review
The purpose of this thesis, three different theories will be discussed, and these include situational /contingency theory as the underpinning theory, great man theory as supporting theory, while agency theory as the complementary.
Situational /contingency theory
Contingency theory centers on adapting situational variables to better fit into a leader’s style. Contingency theorists agree that leadership theories must take into consideration the situation in which leaders operate. For instance, Fred Fiedler’s contingency model assumes that a leader’s preferred style is effectively set and suggests adapting situational elements to achieve better outcomes.
Great man theory
Great man theory proposes that the aptitude for leadership is inborn and inherited. According to this theory, it is either you are born naturally as a leader or you are not. The term ‘great man’ was adopted because it was thought then that leadership was majorly for males, particularly in the military. The great man theory of leadership became well known in the 19th century. The legends behind some of the world's most famous leaders such as mahatma Gandhi, Abraham Lincoln, Alexander the great and Julius Caesar helped contribute to the conception that great leaders are given birth to and not made.
Agency theory
Agency theory is based on the idea that when a company is first established, its owners are usually also its managers. As a company grows, the owners appoint managers to run the company. The owners expect the managers to run the company in the best interests of the owners; therefore, a form of agency relationship exists between the owners and the managers. Many companies borrow, and a significant proportion of the long-term capital of a company might come from various sources of debt capital, such as bank loans, lease finance and bond issues (debentures, loan stock and so on).
Empirical review
Eziokwu & Onuoha, (2021) in rivers state, Nigeria, an examination was conducted into the relationship between the reward system and the organizational performance of deposit money institutions. Pearson’s product moment correlation techniques were used to analyzed data collected. Findings reveals that reward system was dimensionalized using pay/salary as a means of organizational contributed greatly to employee and customer satisfaction. It was suggested that banks in collaboration with top management implement innovative initiatives that recognize non-managerial employee’s accomplishment thus leading to greater performance of the banks.
Directive and employee’s performance.
Nuryanti & Rahmawati, (2016) study titled: “the influence of situational leadership and work environment towards employees’ performance”, this study aimed to clarify the situational leadership, work environment, and employees’ performance, and evaluate the impact of situational leadership and work environment on employees’ performance in service and development sector, and find out the relationship between situational leadership and work environment. This study targeted the employees of the services and business development sector (LPU) of RRI Bandung. The research type is descriptive and verification. The method used is the explanatory survey method with 26 people as saturated sampling. Technical analysis of the data used in this research is multiple linear regressions with spss 21.0 for windows. The result of this study showed that situational leadership has a positive influence on employees, performance, and the work environment has a positive influence on employees’ performance, and both situational leadership and work environment have a positive effect on employees’’ performance, and there is a positive relation between situational leadership and work environment.
Supportive and employee’s performance
Wuryani, (2020) on “analysis of decision support system on situational leadership styles on work motivation and employee performance”, aimed to test the employee's appraisal performance by using situational leadership with work motivation as a variable through a decision support system (DSS). A saturated sample technique from respondents was used in this quantitative research. Smart pls 3.0 was used to analyze the data. The result showed that the decision support system in situational leadership does not have a positive contribution to employee performance.
Extrinsic and employee’s performance
Reza, (2019) on the influence of situational leadership, organizational culture and training on employee performance and work motivation of millennial generation at the inspection office of Bri Malang”, this study aimed to exanimate the effect of situational leadership, training, and organizational culture on work motivation and employee performance at the inspection office of Bri Malang. The partial least square method (pls) was used to analyze the sample of 63 millennial auditors. The result shows that situational leadership has a significant effect on work motivation and employee performance, while the training and organization culture has an insignificant effect on employee performance and the training has a significant effect on work motivation while the organization culture not.
Intrinsic and employee’s performance.
Kuvaas, (2017) investigated the influence of internal and external motivations on employee performance and exposed that both internal and external motivations have a different effect on the job performance of the employee. The findings of the study showed that internal motivation was positively correlated with work performance and has a negative link with turnover intention and burnout. However, extrinsic motivation has a positive relationship with turnover intention and burnout and has a negative correlation with work performance.
Research gap
The gap identified by the researcher, being the question of how leaders in the local government environment use situational leadership to drive the implementation of their mandate, was occasioned by the need to gain insight to critical questions that would challenge notions around the significance or lack thereof of situational leadership in the sector, with directive, supportive, coaching and delegating. These insights would be derived from first-hand accounts of leaders within the organization. There are mixed findings when it comes to individual rewards and their effect on performance. From the review of the above literature, it reveals that empirical data on the effects of situational leadership on performance of employees is able to describe copious performance outcomes, regardless of whether at the organizational levels or individual levels. It is as a result of this that the drive for this study is available as a way to increase empirical evidence of situational leadership reward and employee performance in in the Nigerian banking industry.
Summary of literature review
People are indeed the lifeblood of any organization and it is incumbent upon the leader to create an enabling environment that promotes the organizational values of the institution to ensure that the workforce is capable of consistently performing at optimal levels. Situational leadership influence on employees’ performance within an organization was explored in a dynamic concept.
METHODOLOGY
Research design
This study is also descriptive whereby quantitative research approaches was adopted to gain insight about the role of inclusive leadership on psychological security; it is descriptive in that it described the characteristics of respondents (bougie,2020). The study adopts the descriptive research design for the study since describes the situational leadership reward and employee’s performance.
Area of study
The research population consist of employees of four (4) commercial banks operating in Jos north LGA of plateau state, reasons for focusing on the four commercial bank is because according to central bank rating the four commercial banks falls between the first four banks on the rating (CBN, 2022). The employees were invited to participate in the research survey by filling the questionnaires that were provided to them.
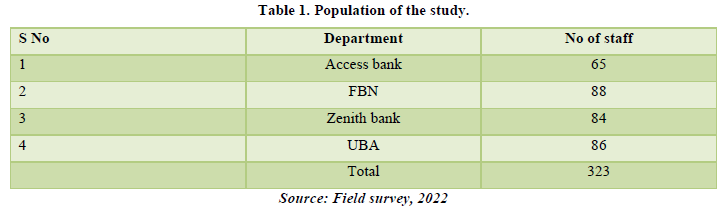
Population of the study
A population is the totality of the objects under the investigation. It is a set of all cases of interest, with respect to this study, the target population will be 323 employees of some selected commercial banks in Jos north local government area of plateau state (Table 1).
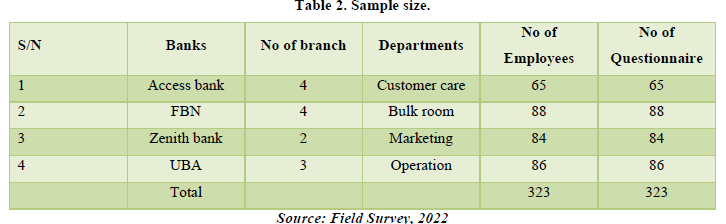
Sample size
According to O’neill (2022) a sample is a group of items, taken from the population for examination. A census eliminates sampling error and provides data on all the individuals in the population. The researcher deemed it fit because it will give opportunity for the researcher to divide participant based on departments (McCumbers, 2020) (Table 2).
Sampling technique
Simple random sampling technique was used to select respondents among employees of some selected commercial banks in Jos north local government area of plateau state, within jos north local government area of plateau state in order to produce more representative and accurate sample. The participants were selected according to the researcher interest in them.
Sources of data
The study collected data from primary source. The data is derived from new or original research study and collected at source, and information is obtained directly from first-hand sources by means such as surveys, observation or experimentation (Stratton, 2022).
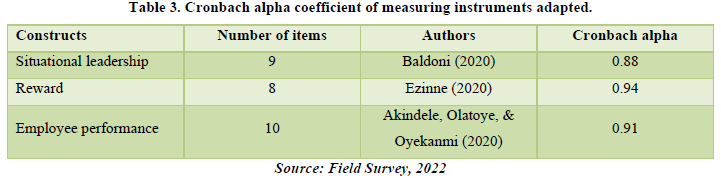
Cronbach alpha coefficient
The Cronbach alpha coefficient of the adapted measuring instruments is obtained in Table 3.
Method of data analysis
The multiple linear regression analysis will be adopted for the testing of hypotheses via the statistical package for social sciences (SPSS) statistics 26. As a set of techniques for studying the straight-line relationships among two or more variables, multiple linear regression analysis estimates the β’s in the equation y j =β0+β1x1j +β 2x2j +---+βpxpj +εj. The x’s are the independent variables (iv’s). Y is the dependent variable. The subscript j represents the observation (row) number.
Model specification
Model specification refers to the determination of which independent variables should be included in or excluded from a regression equation.
Ep= f (sl, rw)
The function model can be transformed into an equation form as thus;
Ep = β0 + β1 sl1 + β2 sl2 + β3 rw1 +β4 rw2+ et
Apriori expectation of the model
Β1, β2 < 0 and β3, β4 > 0
Data Presentation and Analysis
Response rate
A total number of 323 questionnaires was distributed to the target population but only 281 questionnaires were returned. This represents a response rate of 86.99% which was satisfactory to draw conclusions from the study. As Babbie (2012) puts it, a response rate of above 70% is deemed to be very good for analysis.
Profile of the respondents
A total of 281 respondents were the target population for this analysis, the population consists of commercial banks operating in Jos metropolis of plateau state. The questionnaires were distributed as shown in demographic distribution of respondents below:
Demographic distribution of respondents
The respondents were distributed according to the following demographic criteria as shown on Table 4.
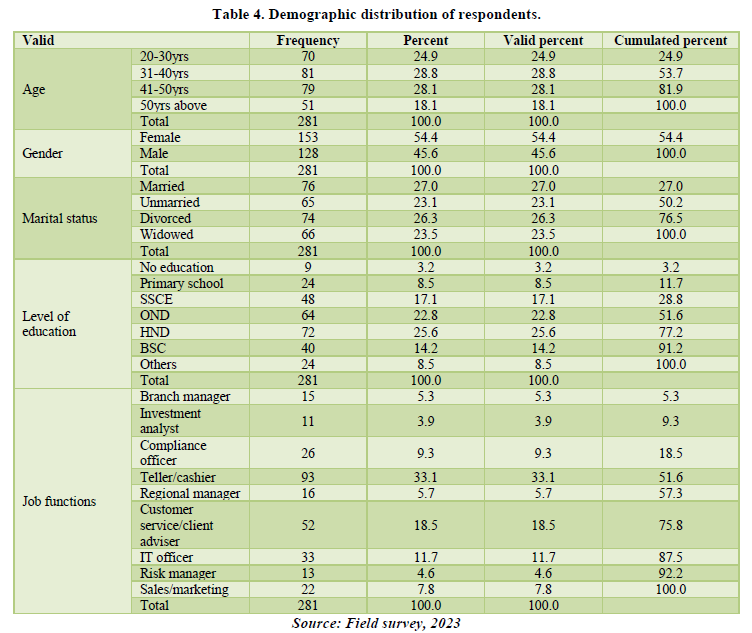
Based on the findings from the descriptive statistics and correlations from Table 5, the independent variables result showed that the mean value for situational leadership dimensions (directive and supportive) (sl) was 24.5231, while reward (intrinsic and extrinsic) (rw) was 33.3167. The dependent variable, employee performance (ep) recorded a value of 29.8185.
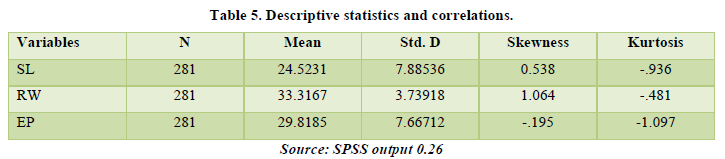
Multicollinearity
Multicollinearity is defined as the degree of correlation among independent variables (Hair et al., 2012). From Table 6 the tolerance level indicated a range between 0.200-0.505 significantly, which is less than 0.7. In the same vein, Vif showed a range of 1.982-4.988 which is less than 5. This result is very good as it showed that there was no multicollinearity issue among the construct used in this study (Hair et al., 2012).
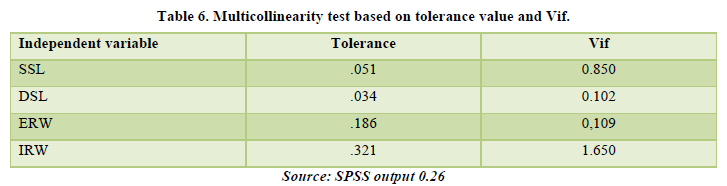
Test of hypotheses
This aspect put forward the research hypothesis, showing the result of the main effect of the independent variable situational leadership (directive and supportive) and reward (intrinsic and extrinsic). In testing the relationships, the significance level was at p< 0.000 and p< 0.001 (Hair et al., 2012). As indicated in Table 7 the four direct relationships between the four dimensions of the independent variable and dependent variable showed a strong positive significant effect, which includes (1) directive situational leadership (sl) and employee performance (ep) (β=0.453: t=0.201 p<0.000) (2) supportive situational leadership (ssl) and employee performance (ep) (β=0.370: t=4.706 p<0.000) (3) extrinsic reward (rw) and employee performance (ep) (β=0.495: t=7.575 p<0.000). (4) intrinsic reward (rw) and employee performance (ep) (β=0.042: t=4.012 p<0.001).
- Hypothesis 1: Based on the result which is positive (β=0.453: t=0.453 p<0.000), the relationship between the variables is significant at p
- Hypothesis 2: Based on the result which is positive (β=0.370: t=4.706 p<0.000), the relationship between the variables is highly significant at p
- Hypothesis 3: Based on the result which is positive (β=0.495: t=7.575 p<0.000), the relationship between the variables is strongly significant at pxtrinsic dimension of reward system, performance increases with 7.575 standard deviation. Therefore, in extrinsic dimension of reward system has a strong impact on employee performance among commercial bank in JOS North LGA of plateau state.
- Hypothesis 4: Based on the result which is positive (β=0.042: t=4.012 p<0.001), the relationship between the variables is significant at pintrinsic dimension of reward system, and an increase with 4.012 standard deviation of performance. Therefore, intrinsic dimension of reward system has a strong impact on employee performance among commercial bank in JOS North LGA of plateau state.
DISCUSSION OF FINDINGS
This study explored situational leadership reward and employee performance in in the Nigerian banking industry: a study of selected commercial banks in JOS. To accomplish this, hypotheses regarding relations between the concepts of the research had been raised and tested using data gathered via questionnaires. The descriptive findings showed high internal consistency for all the scales and reliability for each multi-item scale was assessed using Cronbach’s alpha, where strong reliability is demonstrated with coefficient alpha ranging from 0.75 - 0.94.
Directive dimension of situational leadership and employee performance
H1 in testing this hypothesis, the relationship between directive dimension of situational leadership and employee performance was examined and found significant, showing a positive relationship which means that there is a statistically significant relationship between directive dimension of situational leadership and employee performance because as directive dimension of situational leadership increases, employee performance also increases; and based on these results, h1was rejected. This study is consistent with literature as it is in line with the works of this finding is similar to Ojokuku, et al. (2012) where they found that directive leadership style, in which employees are allowed to have sense of purpose.
Supportive dimension of situational leadership and employee performance
H2 in testing this hypothesis, the relationship between supportive dimension of situational leadership and employee performance was examined and found significant, showing a positive relationship. Based on these results, H2 was rejected. Results from this study proved that supportive dimension of situational leadership is positively correlated with employee performance which is in line with the study of Mungania & Karamja, (2015) found that leadership to be a major factor that affects implementation of strategic plans and concluded that these plans should of essence be both realistic and attainable to allow managers to support decisions and act with operational (r = .68, p < .01). It is also consistent with the empirical work of (smith, 2017), which confirmed that the greater the supportive tendencies of managers with organizational values, the lesser the intention of the individual to quit the organization (y12,3 = - 2.55, p< 0.01). Henkel & Bourdeau, (2018) said that two situational leadership styles (directing and supporting) appearing during the self-assessment by military managers, and showed that this assessment helps managers to have a better understanding of situational leadership styles.
Extrinsic dimension of reward system and employee performance
H3. In testing this hypothesis, the relationship between extrinsic dimension of reward system and employee performance was examined and found significant, showing a positive relationship. Results from this study confirmed that extrinsic reward system has a positive correlational relationship with employee performance. This study is consistent with literature as it is in line with the empirical works of Stajkovic & Luthans, (1998) and Kamau, (2013) who found a positive connection between different forms of extrinsic reward which ultimately affected employee performance and discovered a positive correlation (r = .64, p < .01). This study does not agree with the study of Luthans & Stajkovic, (2006) who saw extrinsic as a tool of invoking better performance among employees. It did not also validate the proposition made by Katru, (2006) that extrinsic reward system was an incentive for improved performance because it increases motivation.
Intrinsic dimension of reward system and employee performance
H4 in testing this hypothesis, the relationship between intrinsic dimension of reward system and employee performance was examined and found significant, showing a positive relationship which means that there is a statistically significant relationship between intrinsic dimension of reward system and employee performance. Based on these results, h4 was rejected. Results from this study were supported by Nakalema, & Ssenyonga (2014), who posited that intrinsic reward framework is a significant viewpoint in an association as it impacts authoritative execution. Results additionally show exceptionally huge and solid connection among acknowledgment and association execution. The most grounded and profoundly huge relationship exists among intrinsic and employee performance. The findings of this study find the support of Rinny, Purba & Handiman, (2020).
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Summary of findings
This study was carried out essentially to examine effect of situational leadership, reward and employee performance: a study of some selected commercial banks in jos. The findings are as follows:
Directive situational leadership was also found to be significantly and positively correlated with employee performance and overall performance, also had a significant positive correlation with employee performance as a whole.
According to the test results of the hypotheses formed in line with the main objective of the research, it was determined that the supportive situational leadership positively impact the employee performance.
It has been revealed that reward system variables such as compensation, training and development, conducive working environment and promotion, opportunities affect the performance of health workers in the study area. Reward system is a vital tool used to not only maximize the performance of employees.
Employees are the most valuable asset of the organization as they take responsibility for enhanced customer satisfaction, quality of products and services and the actualization of organizational goals.
CONCLUSION
From the research findings, it can be deduced that leaders who have a strong desire to achieve better performance from the employees should do more to adopt a situational leadership and reward system approach. An important question is how this reservoir can be tapped. In brief, this study has demonstrated the effectiveness of intrinsic rewards (social recognition and appreciation) and extrinsic rewards (salary, bonus and performance promotion) effect on employee performance in commercial banks.
RECOMMENDATIONS
The following recommendations are made based on the findings of the study:
- Managers expect the employees to perform, as well, while supervisors should create an enabling environment not to discourage work performance.
- Managers should be made to be aware of what is paramount for the employees to be able to perform exceedingly in any giving task.
- The HRM department in conjunction with senior management and trade unions should revise the current salary scale in line with prevailing economic environment.
- The research revealed that bonuses are given to managers.
DIRECTION FOR FURTHER STUDIES
For future researchers can replicate this research model through a longitudinal approach (from time to time), and allow use on other organizations / companies. In addition, future researchers can modify the research model by adding or developing indicators or other variables. This is based on the determinants of employee performance quite a lot and different from the conditions of each other organizations.- Abuzaid, A. N. (2016). Testing the impact of strategic leadership on organizational ambidexterity a field study on the jordanian chemical manufacturing companies. International Journal of Business and Management, 11, 328-339.
- Aifuwa, H. O., Saidu, M., & Aifuwa, S. A. (2020). Coronavirus pandemic outbreak and firm’s performance in Nigeria. Management and human resources research.
- Akor, P. U. (2014). Influence of autocratic leadership style on the job performance of academic librarians in Benue state. Journal of Educational and Social Research, 4, 148-152.
- Armstrong, M (2001). A handbook of human resources management practices. London book power elst.
- Babbie, E. (2012) The practices of social research. 13th edn.
- Barney, J.B. (2001) resource-based theories of competitive advantage a ten-year retrospective on the resource-based view. Journal of Management, 27, 643-650.
- Bass, U. (2008). The bass handbook of leadership theory research and managerial applications New York free press
- Belmejdoub, A. (2015). The leadership journey: A paradigm for developing globally responsible leaders. North Umbria university Newcastle. Master’s thesis pp: 1-29. Accessed on: May 30, 2019. Available online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301675222_the_leadership_journey_a_paradign_for_developing_globally_responsable_leaders
- Bhatti, A., Arif, S., Marium, M., & Younas, S. (2018). The impact of corporate social responsibility (CSR) and relationship marketing on relationship maintainer and customer loyalty by mediating role of customer satisfaction. Journal of Management Info, 4, 19-24.
- Biaga, J.C & Itakpe, S.O (2021) Carried out a study to investigate the reward system and employee performance in the river state oil and gas business.
- Blazi, C. & Awolusi, O. D. (2020). Employee engagement in multinational diverse organization in difficult terrain: A study of non-family station organization. Information Management and Business Review, 12, 45-62.
- Bougie, R., Uma Sekaran, & Wiley, J. (2020). Research methods for business: A skill building approach. John Wiley & Sons Copyright.
- Boukrinaa, O., Kucukboyacib, N. E., & Dobryakovab, E. (2020). Considerations of power and sample size in rehabilitation research. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 154, 6-14.
- Central Bank of Nigeria. (2022). Financial stability report January. Abuja central bank of Nigeria.
- Chemers, M. M. (2000). Leadership research and theory a functional integration. Group Dynamics Theory Research, and Practice, 4,27-43.
- Cherry, K. (2020). The great man theory of leadership. Available at: https://www.verywellmind.com/the-great-man-theory-of-leadership-2795311
- Cheung, M.F.Y. and Wong, C. (2011). Transformational leadership, leader support, and employee creativity. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 32, 656-672.
- Chong, L. K. (2010). Education: Let’s set it right. Available online at: http://www.nst.com.my/nst/articles/20100908000851/article/
- Cooper, D.R. & Schindler, P.S. (2003) Business research methods. 8th edn, Mcgraw-Hill Irwin, Boston.
- Conger, R. D., Conger, K. J., & Martin, M. J. (2010). Socioeconomic status, family processes, and individual development. Journal of Marriage and Family, 72, 685-704.
- Eziokwu, C. D., & Onuaha, B. C. (2021). Reward systems and organizational performance of deposit money banks in river state. African Journal of Business and Economic Development, 1, 11-26.
- Fiedler, F. (1964). A contingency model of leadership effectiveness. In l. Berkowitz (ed.), advances in experimental social psychology. New York academic press. 1: 149-190.
- Fu-Jin, W., Shieh, C. and Tang, M. (2010) Effect of leadership style on organizational performance as viewed from human resource management strategy. African Journal of Business Management, 4, 3924-3936.
- Grint, Keith (2011). A history of leadership. In Bryman, Alan and Collinson, David and Grint, Keith and Jackson, Brad and Uhl-Bien, Mary.
- Gimuguni, L., Nandutu, J., & Magolo, A. (2014). Effect of leadership styles on performance of local governments in Uganda, Acase of Mbale District.
- Glynn, M. A., & Dejordy. R. Khurana, R., Nohria, N. (2010). Leadership through an organization behavior lens in.
- Gumusluoglu, L. and Ilsev, A. (2009) Transformational leadership, creativity, and organizational innovation. Journal of Business Research, 62, 461-473.
- Ghazzawi, K., El Shoughari, R., & El Osta, B. (2017). Situational leadership and its effectiveness in rising employee productivity: A study on north Lebanon organization. Human Resource Management Research, 7, 102-110.
- Greyling, E. (2012). Opportunities for employment creation through SME development in the construction sector free state. International Labour Organization, Pretoria.
- Hair, J.F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C.M. & Mena, J.A. (2012). An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 40, 414-433.
- Harold, C. M., & Holtz, B. C. (2015). The effects of passive leadership on workplace incivility. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 36, 16-38.
- Henkel, T., & Bourdeau, D. (2018). A field study an examination of managers' situational leadership styles. Journal of Diversity Management.
- Hersey, P., & Blanchard, K. (1969). Life cycle theory of leadership. Training and Development Journal, 23, 26-35.
- Hong, Q. N. (2018). Revision of the mixed methods appraisal tool a mixed method study doctoral dissertation Department of family medicine, McGill university, Montréal.
- Iyiola, A. T., Olatoye, O. A., & Oyekanmi, T. T. (2020). Impact of performance appraisal strategy on employee productivity evidence from selected Nigerian banks. Journal of Management and Social Sciences, 9, 770-783.
- Kamau, S. M. (2013). Competitive strategies adopted by private universities in Kenya. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Nairobi.
- Kuruzovich J., Paczkowski W., Golden T. D., Goodarzi S., & Venkatesh V. (2021). Telecommuting and job outcomes a moderated mediation model of system use, software quality, and social exchange. Information and Management, 58, 103431.
- Kuvaas, B., Buch, R., Weibel, A., Dysvik, A., & Nerstad, C. G. (2017). Do intrinsic and extrinsic motivation relate differently to employee outcomes. Journal of Economic Psychology, 61, 244-258.
- Lin, H.-F. (2007) Knowledge sharing and firm innovation capability an empirical study. International Journal of Manpower, 28, 315-332.
- Lynch, M. (2015). More play please the perspective of kindergarten teachers on play in the classroom. American Journal of Play, 7, 347-370.
- Matira, K. M., & Awolusi, O. D. (2020). Leaders and managers styles towards employee centricity: a study of hospitality industry in United Arab Emirates. Information Management and Business Review, 12, 1-21.
- Mcgrath, G.R.& Macmillan, I.C. (2000). entrepreneurial mindset strategies for continuously creating opportunity in an age of uncertainty. Harvard business school press books.
- Mccumbers, S, (2020) Descriptive research. Available online at: https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/descriptive-research.
- Michelle R. (2019). How does an employee reward system promote organizational performance? Available online at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/goal-setting-rewards-organizational-behavior-55360.html
- Muhammad Tahir Khan Farooqi, Dr. Asif Iqbal, Dr. Shehzad Ahmed (2020). impact of teaching methods on achievement score of students at university level. Elementary Education Online, 19, 5427-543.
- Muhammad Ahmad Mazher. (2022). Exploring relationship between intrinsic rewards extrinsic rewards, and employee performance in university academics. East Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research, 1, 2691-2706.
- Mungania, V. N., & Karamja, E. (2015). The influence of the external environment on the Myers, m. (2020). Qualitative Research in Business Management. Thousand oaks sage.
- Nakalema, G., & Ssenyonga, J. (2014). Academic stress its causes and results at a Ugandan University. African Journal of Teacher Education, 3, 3.
- Noko, E., & Nwuzor, J. (2021). Employee and organizational performance employees’ perception of intrinsic and extrinsic rewards system.
- Nuhu, K. (2004). Effect of leadership styles on employee performance in Kampala district council. Doctoral dissertation, Makerere university.
- Nuryanti, B. L.& Rahmawati, R. (2016). The influence of situational leadership and work environment towards employees’ performance. 15, 540-543.
- Nyaberi, J. P. L. (2020). Leadership style and performance of state corporations of Kenya. The Strategic Journal of Business & Change Management, 7, 1515-1522.
- Ojokuku, R. M., Odetayo, T. A., & Sajuyigbe, A. S. (2012). Impact of leadership style on organizational performance a case study of Nigerian banks. American Journal of Business and Management, 1, 202-207.
- O’Neill, G. (ed.). (2011). A practitioner’s guide to choose of assessment methods within a module. UCD teaching and learning.
- Pahi, M. H., Hamid, K. A., & Khalid, N. (2016). Save talent of banking sector of Pakistan: Mediating job satisfaction between job stress and employee turnover intention. International Review of Management and Marketing, 6, 617-624.
- Pahi, M. H., & Hamid, K. A. (2016). The magic of destructive leadership: Laissez-fair leadership and commitment to service quality. International Journal of Economic Perspectives, 10.
- Pattanayak, b. (2005). Human resource management 3rd new delhi phi learning private limited.
- Prasetya, A. & Kato, M. (2011). The effect of financial and non-financial compensation to the employee performance. The 2nd International Research Symposium in Service Management. Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
- Rahadiyan, A., Triatmanto, B., & Respati, H. (2019). The effect of motivation and situational leadership style towards employee performance through work satisfaction at developer company. International Journal of Advances in Scientific Research and Engineering-Ijasre, 5, 249-256.
- Rasool, H. F., Arfeen, I. U., Mothi, W., & Aslam, U. (2015). Leadership styles and its impact on employee's performance in health sector of Pakistan. University Research Journal, 5, 08
- Reza, M. H. (2019) Components of transformational leadership behavior. Available online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333798276_components_of_transformational_leadership_behavior
- Richard, O.C. (2000) Racial diversity, business strategy, and firm performance: a resource-based view. Academy of Management Journal, 43, 164-177.
- Ridlwan, M., Purwandari, D. A., & Syah, T. Y. R. (2021). The effect of situational leadership and organizational culture on employee performance through job satisfaction. International Journal of Multicultural and Multireligious Understanding, 8, 73-87.
- Rinny, P., Purba, C. B. & Handiman, U.T. (2020). The influence of compensation, job promotion and job satisfaction on employee performance of Mercubuana university. International Journal of Business Marketing and Management, 5, 39-48.
- Saunders, M., Lewis, P. And Thornhill, A. (2014). Research methods for business students. Pearson education limited, London.
- Schriesheim, C. A., Castro, S. L., & Cogliser, C. C. (1998). Leader-member exchange (LMX) research: A comprehensive review of theory, measurement, and data-analytic practices. The Leadership Quarterly, 10, 63-113.
- Smith, J. (2017). Mixed methods research expanding the evidence base. Evidence-Based Nursing, 20, 74-75.
- Squires, B., & Elnahla, N. (2020). The roles played by boards of directors: An integration of the agency and stakeholder theories. Transnational Corporations Review, 12,126-139.
- Stajkovic, A. D., & Luthans, F. (1998). Social cognitive theory and self-efficacy going beyond traditional motivational and behavioral approaches. Organizational Dynamics, 26, 62-75.
- stratton, James. (2022). Intentional and incidental vocabulary learning the role of historical linguistics in the second language classroom. The Modern Language Journal, 106, 837-857.
- Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using multivariate statistics New York, Allyn and Bacon.
- Thompson, G.& Vecchio, R.P. (2009). Situational leadership theory a test of three versions. Leadership Quarterly, 20, 837-848.
- Waruni, A.E (2014). Impact of rewards on employee performance: With special reference to. Electro ico. Reshaping management and economic.
- Wuryani, E., Rodli, A. F., Sutarsi, S., Dewi, N. N., & Arif, D. (2021). Analysis of decision support system on situational leadership styles on work motivation and employee performance. Management Science Letters, 365-372.
- Yasmeen, R., Farooq, U. & Asghar, F. (2013). Impact of rewards on organizational performance: Empirical evidence from telecom sector of Pakistan. Journal of Basic and Applied Science, 3, 938-946.
- Yukl, G. (2011). Contingency theories of effective leadership. The Sage Handbook of Leadership, 24, 286-298.
- Zigarmi, D & Roberts, T.P. (2015). The impact of dispositional cynicism on job specific affect and work intentions. International Journal of Psychology, 49, 381-389.



