Research Article
Job: A Time to Savor
5409
Views & Citations4409
Likes & Shares
Job satisfaction has become a critical issue for nursing educational institutes because of the shortage of capable nursing tutors which indirectly has detrimental effect on patient care as the students learning gets hampered.
Personal experience as an administrator and professor in the nursing education field has showcased that the current nursing education lags the expectations of the hospital authorities. The employers and hospital administrators require to retain and prepare educators through orientation and induction before placing them for student teaching. This entails additional responsibility and requires additional time and energy. The researcher therefore undertook the study to assess the level of job satisfaction among nursing educators. The Objectives of the study were:
- To identify the level of job satisfaction among the nursing educators.
- To identify the reforms/ suggestions necessary for job satisfaction.
- To assess the association of job satisfaction with faculty turnover.
The Research Approach used was Descriptive, exploratory. Research Design: Survey. The study was conducted using google form and then sharing it with all the teaching faculty. Sampling technique was Purposive sampling technique was utilized.
Significant Findings: Majority of the faculty feel excellent in terms of work distribution, work environment, team spirit, recognition provided and guidance and support. The faculty is not contended in terms of remuneration, performance feedback, growth opportunity and the overall benefits provided by the institute. The study showed that majority of the faculty were contended with the job and there was very strong association with faculty turnover.
Keywords: Job satisfaction, Efficiency
INTRODUCTION
“Pleasure in the job puts perfection in the work.” - Aristotle
It is very true what Aristotle said about the job contentment. Without job satisfaction and contentment, no employee will put in their best efforts. Thus, the work culture, environment needs to be considered by the managers for the progress in the institute. Job satisfaction is defined as the extent to which an employee feels self-motivated, content & satisfied with his/her job.
Job satisfaction is a pleasurable or positive emotional state resulting from the appraisal of one’s job or experience like working environment, nature of work, pay scale, promotion, supervision, fringe benefits, contingent rewards, colleagues and communication [1].
Job satisfaction has become a critical issue for nursing educational institutes because of the shortage of capable nursing tutors which indirectly has detrimental effect on patient care as the students learning gets hampered [2]. Nursing educators are the bride stone for shaping the right kind of skill, knowledge, attitude among the budding nurses. The educators will be able to work effectively and efficiently if they are contended at work place. Those employees who feel happy and content in their roles are much more likely to approach the tasks that they need to carry out with enthusiasm and dedication.
HRD is the key to develop competent, highly skilled and technically sound personnel needed for greater productivity and efficiency in any organization. It is especially true in the service oriented organization like university, where improvements in service have to be made to meet the expectations of the society and the country [3].
The study done by Shobha and Supriya revealed that there was evidence that there are many factors which can affect the job satisfaction level among nurses, which will in turn affect the quality of patient care and health organization too. Thus importance should be given towards the safety issues in their job, with alleviation of safety hazards. A periodical revision of pay and benefits will also increase the satisfaction level. Working relationships, support of management, and supervision should be also considered and emphasized for better nursing future [4].
A study to assess the level of job satisfaction among the nursing personnel working in clinical sector and educational institutions was undertaken by Sanjay P. The 100 samples were selected with 50 samples each from healthcare and educational institutions by using non-probability; convenient sampling technique. The tool used was modified Minnesota Job Satisfaction scale. Results: the results revealed that 23 (46%) of nursing personnel working in healthcare institutions are satisfied with their overall job whereas 28 (56%) are satisfied with their overall job in educational institutions and there was no significant statistical difference found between the level of job satisfaction among two groups [5].
Thus, overall job satisfaction is an important consideration that will affect the overall upliftment of the institute.
NEED FOR THE STUDY
More than any factors managers should consider the modification of working environment and group cohesions rather than trying to modify nurse educators to retain and maintain more experienced teachers for the organizations.
Employee job satisfaction is the fulfillment, gratification, and enjoyment that comes from work. It is not just the money or the fringe benefits, but the feelings employees receive from the work itself. The most used research definition of job satisfaction is by Locke who defined it as “a pleasurable or positive emotional state resulting from the appraisal of one’s job or job experiences”. Implicit in Locke’s definition is the importance of both effect, or feeling, and cognition, or thinking. When we think, we have feelings about what we think [6]. In another way, it is defined simply as how people feel about their jobs and different aspects of their jobs. It is the extent to which people like (satisfaction) or dislike (dissatisfaction) their jobs [7]. Wikipedia also defines job satisfaction as a pleasurable emotional state resulting from the appraisal of one’s job, an affective reaction to one’s job, and an attitude towards one’s job.
The ability to produce, the quality of the work, the opportunity to learn and express creativity, the sense of pride in their profession, the recognition for a job well done, the ability to work well in a team, the social satisfaction derived from relationships at work, the opportunity to experience personal growth and the rewards from a physically supportive work environment, and autonomy are all factors that impact job satisfaction [8].
The job stress significantly influences the job satisfaction among the nurses albeit there are subjectivity and individual differences in the experience of stress. Identifying stress at the earliest and paying attention to manage and overcome it may have an impact on their personal life and professional outcome in terms of quality of service and patient care [9].
Hackman and Oldham proposed the job characteristics model, which is widely used as a framework to study how particular job characteristics impact job outcomes, including job satisfaction. The model states that there are five core job characteristics (skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback) which impact three critical psychological states (experienced meaningfulness, experienced responsibility for outcomes, and knowledge of the actual results), in turn influencing work outcomes (job satisfaction, absenteeism, work motivation, etc.) [10]. Job satisfactions describes how content an individual is with his or her job. The happier people are within their job, the more satisfied they are said to be. Job satisfaction is not the same as motivation, although it is clearly linked. The most common way of measurement of job satisfaction is the use of rating scales where employees report their reactions to their jobs. Questions relate to rate of pay, work responsibilities, variety of tasks, promotional opportunities in the work itself, and co-workers.
In a study done by Sasmita Das, out of 10 different factors influencing job satisfaction, specific factors were: Safety issues, Poor communication and cooperation, Pay and benefits issues, Opportunities for professional upgrade, Composite satisfaction and working relationships [11].
A study was done to identify role of intrinsic motivation on employees’ job satisfaction and Quality of Work Life [12].
A systematic approach to education is needed to facilitate the educators to bridge theory, research and practice as well as create a starting point for reflection [13]. It then becomes the responsibility of the student to utilize the system, seriously reflect and ultimately be accountable for their learning.
The findings in a study indicated that maximum numbers of respondents (faculty members) were satisfied with their Performance Appraisal System. The findings also revealed that there was a positive relationship between Employee satisfactions on Performance Appraisal System with Fairness of the system [14].
Personal experience as an administrator and professor in the nursing education field has showcased that the current nursing education lags the expectations of the hospital authorities. The employers and hospital administrators require retaining and preparing educators through orientation and induction before placing them for student teaching. This entails additional responsibility and requires additional time and energy.
The investigator therefore felt it necessary to assess the lacunaes in the and identify the reforms necessary to improve nursing education in totality.
As an investigator, it was felt that identifying the level of job satisfaction could help the institute in reforming the policies and ensure that the faculty works effectively and efficiently.
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
The study is based on Systems Theory. The systems theory has major 3 components: Input, Process and Output. In this study,
- Input: The inputs in this study are the responses that are provided by the respondents. This information provided will then act as tool for making necessary changes in the organization.
- Process: In this study, the process refers to the information that is received from the respondents through the prepared tool. In this case, it is the responses to the rating scale that was administered.
- Output: The data gathered is the output. This data gathered will then be evaluated and be utilized further to make changes in the system at individual, organization and policy level.
Thus, there is a continuous assessment and evaluation which will lead to change in the hope of improving the job satisfaction in the institute.
PROBLEM STATEMENT
A study to assess the level of job satisfaction among nursing educators.
Objectives
- To identify the level of job satisfaction among the nursing educators.
- To identify the reforms/ suggestions necessary for job satisfaction.
- To assess the association of job satisfaction with faculty turnover.
Operational Definition
- Assess: In this study, assess refers to identifying the level of job satisfaction among the employees of the selected institute.
- Job Satisfaction: In this study, the job satisfaction refers to the various factors that lead to job contentment.
The job satisfaction was measured using rating scale for the various factors on which job satisfaction depends. The factors considered in the study were: work distribution, work environment, remuneration, resources, performance feedback system, growth opportunity, team spirit, support, recognition, guidance by seniors. 5-point rating scale was used (Excellent, Very Good, Good, Average, Poor)
- Level: In this study, level refers to the grade that the employee has provided to each area of job satisfaction. The grade could be excellent, very good, good, average or poor.
- Employees: In this study, the employees refer to the entire teaching faculty who have completed B.Sc/ P.B. B.Sc/ M.Sc/ P.hd in nursing and are involved in teaching nursing curriculum to the nursing students.
Assumption:
- Job satisfaction affects the morale and working of an employee.
- The level of job satisfaction could be assessed by rating scale.
- Job satisfaction leads to work efficiency.
- Job satisfaction has an effect on employee turnover.
Delimitation:
- The study findings are restricted only to one selected nursing institute.
- The study is only using rating scale for assessing the job satisfaction.
- The data gathered is only through self-reporting.
- Research Approach: Descriptive, exploratory
- Research Design: Survey
- Setting of the study: The study was conducted using google form and then sharing it with all the teaching faculty.
- Sampling technique: Purposive sampling technique was utilized.
- Inclusion criteria for sample selection: All the faculty who are. teaching in either GNM/ Basic B.Sc nursing program)
- Exclusion criteria for sample selection: Non-teaching and supportive staff were not included as part of the study.
- Tool for data collection: Online Self reporting questionnaire (Google form)
- Tool description: The questionnaire used was in online mode. Google form was created which had 3 sections. Section 1 comprised of demographic data, section 2 was the rating scale to score the various factors that affect job satisfaction and section 3 comprised of open ended questions to identify their overall experience in the institute, strengths and improvement areas of the institute.
- Technique for data collection: Self reporting technique was used for data collection.
- Data Collection process: After the form was prepared and validated by experts, the form was shared among the faculty and they were asked to complete it within a specified time period. Online mode was used to maintain the confidentiality of the employee and the responses provided by the faculty.
The faculty were informed that the responses will be kept discreet and will not affect their personal performance appraisal.
SIGNIFICANT FINDINGS
Demographic data:
- Majority of the educators had completed M.Sc Nursing. (78%).
- 3 % of the faculty had served the institute for more than 5 years.
Job satisfaction:
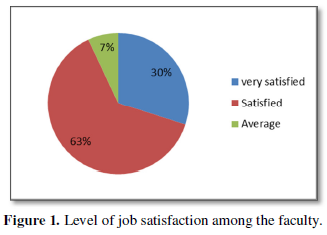
Table 1 shows that:
- Majority of the faculty feel excellent in terms of work distribution, work environment, team spirit, recognition provided and guidance and support.
- The faculty is not contended in terms of remuneration, performance feedback, growth opportunity and the overall benefits provided by the institute.
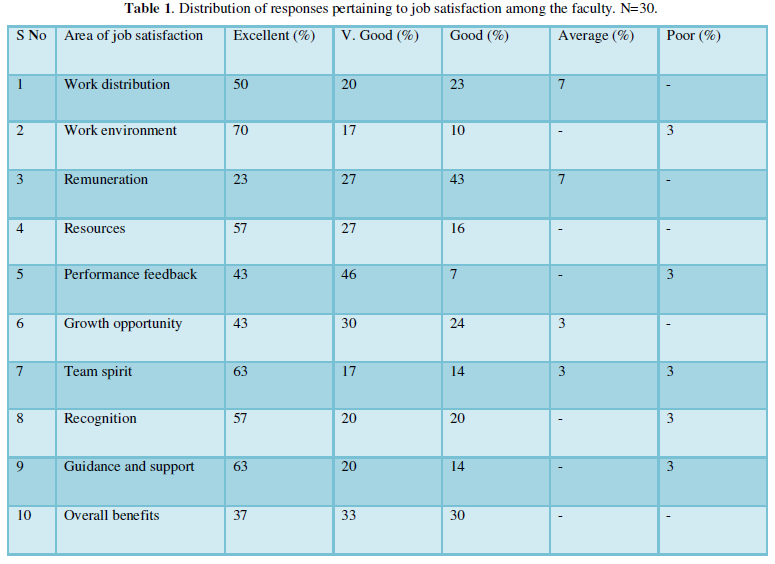
The study revealed in Figure 1 is that 30% of the faculty were very satisfied with their job; whereas 63% were satisfied. Only 7% of the faculty were not contended with the job. Thus, overall level of job satisfaction among the faculty was seen.

SUGGESTIONS PROVIDED BY THE FACULTY
- 13% of the faculty suggested improving the resources available in the institute. (Especially computers, internet and WI Fi facility).
- 7% of the faculty felt that leadership opportunities should be provided.
- 13% of the faculty felt that the institute needs to look into creating higher posts and provide more opportunities for growth. Another study done revealed in terms of ranking dimension teaching, research and pay is the most preferred whereas supervision, role of co-workers and infrastructure are amongst the least preferred dimension. Also on basis of demographic variable senior faculties in terms of age drawing higher salaries are most satisfied [15].
- Only 7% faculty felt that there is work overload.
Association of job satisfaction with turnover:
The study showed that majority of the faculty were contended with the job and there was very strong association with faculty turnover.
Limitations of the study:
- The data gathered cannot be completely reliable due to subjectivity issues and personal barriers.
- The data is gathered only from one institute.
- Data is gathered by using only rating scale as a tool.
SUGGESTIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
- A similar study can be used over a period of time to assess the retention rate of an institute.
- A comparative study could be done using data of different institutes with varied administrative control.
- Similar study using tools other than rating scale could be done.
- A similar study using various Human resource techniques could be done and its impact could be assessed.
Significance of the Study
The lack of research addressing the factors that influence nurse educators job satisfaction and intention to turnover is a problem because if administrators do not know what the educators want, they cannot make changes to better satisfy them. This study provided information that is important to practice, nursing administration and policy maker, and nursing education.
For Policy Maker: This study will provide input for policy maker on changing worker characteristics, changing job characteristics, and working environment adjustment. It may also help in job placement strategies to retain more staff. Again, for education and training of staff this study may indicate the area of interest for provision of problem solving education. A study done by SurabhiBhargava too demonstrated that Staff development program is effective in increasing the level of communication skills and job satisfaction of staff nurses’ [16].
CONCLUSION
To conclude, it is evident that the faculty are mostly contended with majority of the factors affecting job satisfaction; but the institute requires to undertake measures to provide resources necessary for teaching learning process and address the growth opportunity issues to ensure that the faculty retention is strong.
- Samuel PK, Rupa G (2017) A Study to Assess Level of Job Satisfaction and Subjective Wellbeing of Teaching Faculty Employed in Selected Colleges of Nursing at Pandalam, Pathanamthitta District, and Kerala. Asian J Nurs Educ Res 7(2): 222-224.
- Al Maqbali MA (2015) Job Satisfaction of Nurses in a Regional Hospital in Oman: A Cross-Sectional Survey. J Nurs Res 23(3): 206-2
- Tiwari U (2014) Training and Development, Job Satisfaction and HRD Climate in a Service Organisation. Asian J Manag 5(4): 431-434.
- Jagadale S, Chinchpur S (2016) A Descriptive Study to Assess the Job Satisfaction among the Nursing Staff of Selected Hospital of Pune City. Asian J Nurs Educ Res 6(2): 204-208.
- Peerapur S (2019) Job Satisfaction among the nursing personnel working in Clinical and Educational Sector at selected health care and Educational Institutions in Hubli and Dharwad City, Karnataka. Asian J Nurs Educ Res 9(1): 23-26.
- Locke EA (1976) The Nature and Causes of Job Satisfaction. In: Dunnette, M.D., Ed., and Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology. 1: 1297-1343.
- Spector PE (1997) Job Satisfaction: Applications, Assessment, Causes and Consequences, Sage Publications. pp: 104.
- Linda P (2001) Conducting Hospital Employee Satisfaction Surveys, MS Mountain States Group, 1st
- Suni MS, Nirmala V, Sikkandar S (2017) Stress and Job Satisfaction among Staff Nurses. Asian J Nurs Educ Res 7(1): 31-34.
- Hackman JR, Oldham GR (1974) The job diagnostic survey: An instrument for the diagnosis of jobs and the evaluation of job redesign projects. Department of Administrative Sciences: Yale University.
- Das S, Baby P (2014) Correlation between Organizational Stress and Job Satisfaction among Registered Nurses in Selected Hospital. Asian J Nurs Educ Res 4(1): 45-49.
- Rajput S, Singhal M, Tiwari SK (2016) Job Satisfaction and Employee Loyalty: A study of Academicians. Asian J Manag 7(2): 105-109.
- Martin GW, Mitchell G (2001) A study of critical incident analysis as a route to the identification of change necessary in clinical practice: Addressing the theory-practice gap. Nurs Educ Pract 1(1): 27-34.
- Mahajan S, Kumar S (2018) A Study on Impact of Job Satisfaction on Employee Performance in Organization. Asian J Manag 9(3): 1046-1054.
- Chaturvedi V, Sethi MK (2010) Job satisfaction among academicians: A study with reference to Management Colleges (both Government and Private) in Faridabad. Asian J Manag 1(1): 4-7.
- Bhargava S (2019) Effect of Staff Development Programme on Staff Nurses’ Communication Skills and Job Satisfaction at Javitri Hospital Lucknow, U.P. Asian J Nurs Educ Res 9(3): 297-300.
QUICK LINKS
- SUBMIT MANUSCRIPT
- RECOMMEND THE JOURNAL
-
SUBSCRIBE FOR ALERTS
RELATED JOURNALS
- Journal of Womens Health and Safety Research (ISSN:2577-1388)
- Proteomics and Bioinformatics (ISSN:2641-7561)
- Journal of Agriculture and Forest Meteorology Research (ISSN:2642-0449)
- Journal of Genomic Medicine and Pharmacogenomics (ISSN:2474-4670)
- Food and Nutrition-Current Research (ISSN:2638-1095)
- Advances in Nanomedicine and Nanotechnology Research (ISSN: 2688-5476)
- Journal of Veterinary and Marine Sciences (ISSN: 2689-7830)



