978
Views & Citations10
Likes & Shares
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animal material
Wistar rats weighing between 120 and 140g and aged 4 months were used. These rats were supplied by the animal house of the Normal Superior School (ENS) of the Université Marien Ngouabi.
Plant material
Root barks of Rauvolfia obscura K. Schum (Apocynaceae) were used. The roots were harvested in Gamboma, 365 km from Brazzaville in the Plateaux department, in March 2023. Identification was carried out by systematist botanists from the Faculty of Science and Technology, then completed at the botany laboratory in Brazzaville, where a sample was deposited under number: IEC001856 dated 9/12/96.
Methods
Preparation of aqueous extract
Fifty grams (50 g) of Rauvolfia obscura powder were macerated in 500 ml of distilled water for 48 h. After filtration through absorbent cotton and “Wattman” filter paper, the macerate was concentrated in a water bath thermostated at 55°C, to obtain the brown-colored aqueous extract. The aqueous extract obtained was stored in a flask. This aqueous extract enabled us to carry out our laboratory work:
- Study of anti-hyperglycemic activity in wistar rats
- This study was carried out according to the method described by Ampa [3]
- 25 rats were divided into 5 batches, each containing five (5) rats
- Batch 1 (negative controls): animals received distilled water at a dose of 0.5ml/100kg
- Batch 2 (positive controls): animals received metformin (reference molecule) at a dose of 10mg/kg
Batches 3,4,5: animals received aqueous extract of Rauvolfia Obscura root bark at doses of 100, 250 and 500mg/kg respectively. Temporary hyperglycemia was induced beforehand in each rat, by overloading them with glucose (10%) by intragastric gavage at a dose of 3g/kg. Glycemic monitoring of each animal was carried out before administration of the products, then 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 3 h, 4 h and 5 h after administration of the aqueous extract of Rauvolfia obscura root bark.
Hypoglycemic activity in rats
This study was carried out according to the method described by Ampa [3].
25 rats were divided into 5 batches, each containing five (5) rats as follows:
Batch 1 received distilled water (0.5ml /100g);
Batch 2 received metformin (10mg/kg);
Batches 3,4,5: received aqueous extract of Rauvolfia Obscura root bark (100, 250 and 500 mg/kg).
The animals were fasted 18 hours before administration a of the aqueous plant extract.
Blood glucose levels were recorded for each animal before administration, and 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 3 h, 4 h and 5 h after administration.
Phytochemical profile of Rauvolfia obscura K. Schum root bark
Chemical screening of Rauvolfia obscura root bark powder was carried out using classical phytochemical tests based on staining and precipitation reactions [4].
RESULTS
Anti-hyperglycemic effect of Rauvolfia obscura aqueous extract in wistar rats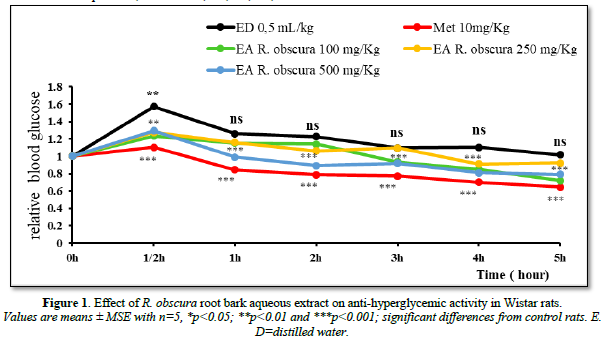
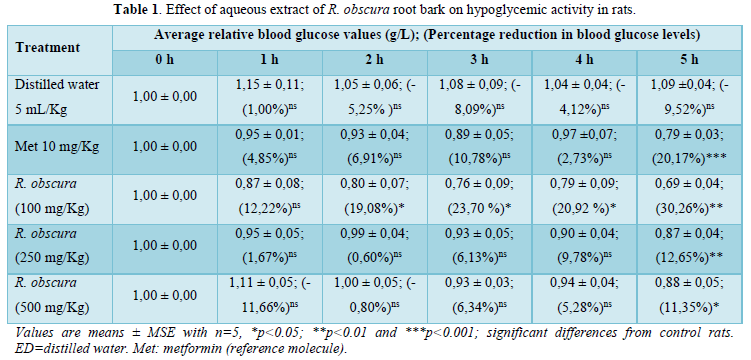
Hypoglycemic effect of aqueous extract of Rauvolfia obscura in Wistar rats
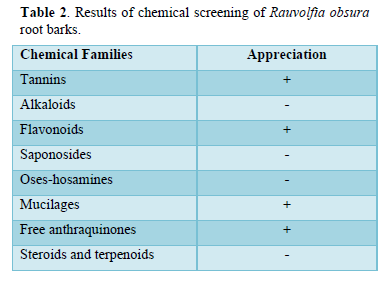
Phytochemical profile results (Table 2)
DISCUSSION
The aim of the present study was to contribute to the treatment of glycemia using Rauvolfia obscura root bark in wistar rats. Administration of the aqueous extract of Rauvolfia obscura root barks (100, 250 and 500 mg/kg) in rats made hypertensive by glucose overload (3g/kg CP), showed a highly significant (***P≤0.001) decrease in blood glucose levels (Figure 1). Analysis of these results shows that this reduction is dose-dependent. Thus, this decrease occurs from: 3, 4 and 1 h, respectively at doses of 100, 250 and 500 mg/kg. The 500 mg/kg dose is therefore the most effective, as it reduces blood glucose levels at an early stage. At this dose, the aqueous extract of Rauvolfia obscura roots has an action similar to that of metformin (10mg/kg). Metformin reduces hepatic glucose production and, to a lesser extent, gastrointestinal glucose absorption and increases glucose utilization by peripheral tissues [5]. The results of this study are similar to those of N'doua et al [6] on the hypoglycemic and anti-hyperglycemic effects of the 70% ethanolic extract of the roots of Rauvolfia vomitoria afzel (apocynaceae), which also showed a decrease in blood glucose levels caused by glucose overload. In this study, the hypotensive effect of Rauvolfia obscura aqueous extract was also evaluated. Administration of Rauvolfia obscura aqueous extract (100, 250 and 500 mg/kg) to normoglycemic rats produced a non-significant (P≤0.05) decrease in blood glucose levels (Table 1). The reduction in blood glucose is explained by the effect of the plant. The results of this study once again confirm the findings of the previous study discussed above. These results suggest that, at this stage of the study, the aqueous extract of Rauvolfia obscura root bark has anti-hyperglycemic properties. The chemical profile carried out on the plant's root bark for this study reveals the presence of the chemical family’s free tannins, flavonoids, muscillages and Antraquinone (Table 2). Numerous studies on aqueous extracts of medicinal plants have shown that flavonoids are responsible for lowering blood sugar levels when these extracts are administered to hyperglycemic rats, as in the case of aqueous extracts of Spondias purpurea L [7]. and Vernonia colorata [8]. The roots of Rauvolfia obscura have hypoglycemic properties, and are recommended for diabetics.
CONCLUSION
At the end of this study on the anti-hyperglycemic and hypoglycemic activity of the aqueous extract of Rauvolfia obscura root barks in wistar rats. It should be noted that administration of the aqueous extract at different doses (100, 250 and 500 mg/kg), causes a significant (***p<0.001) decrease in blood glucose levels at doses of 100 mg/kg from 3 h, 4 h and 5 h; 250 mg/kg from 4 h and 5 h; and 500 mg/kg from 1 h, then continuing until 5 h.
In normoglycemic rats, administration of the aqueous extract at different doses resulted in a non-significant (*p<0.05) increase in blood glucose levels at 500 mg/kg after 1 h, returning to the initial value of 1.00 after 2 h. However, there was a non-significant (*p<0.05) decrease in blood glucose levels at 100 and 250 mg/kg in normoglycemic rats. The aqueous extract of Rauvolfia obscura root bark is recommended for people suffering from hyperglycemia. Rauvolfia obscura root bark contains tannins, flavonoids, muscillages and free anthraquinones. Flavonoids are therefore responsible for the anti-hyperglycemic activity observed with olante root bark. Rauvolfia obscura roots are a good remedy for the treatment of hyperglycemia.
- Atlas (2013) Diabetes of the International Diabetes Federation. 6th
- Ondele R, Ossibi AWE, Bassoueka D’AJ, Peneme MB, Elion Itou RDG, et al. (2015) Acute toxicity and aphrodisiac effect of the aqueous extract of rauvolfia obscura k. Schum (apocynaceae). Afrique Sci 11(3): 172-180.
- Ampa R (2014) Extracts of Trilepisium madagascariense D.C. Leeuwenberg (Moraceae) leaves: Evaluation of antidiabetic, antioxidant and toxic activities, and prevention of complications related to diabetes mellitus in rats. Thesis For the award of the Doctorate Degree of the Marien NGOUABI University pp: 199.
- Ntumbula MA, Zabo IA, LososoMK, Otono FB, Nzambi1 CTP (2014) Chemical Study and Clinical Trial of an Antidiabetic Recipe Madose Cultural and Scientific Review pp: 1-7.
- Foretz M, Viollet B (2009) Hepatic mechanism of metformin action in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med Metabol Dis 3(1): 5-111.
- N’doua LAR, Abo KJC, Aoussi S, Gbogbo M, Yapo AP, et al. (2015) Effets hypoglycemique et antihyperglycemique de l’extrait ethanolique 70% de racines de Rauvolfia vomitoria afzel (apocynaceae). Eur Sci J 11: 176-190.
- Diatta A, Manga A, Gassama A, Lavaud C (2017) Antihyperglycemic Activity and Structural Elucidation of Compounds Isolated from the Leaves of Spondias Purpurea L. (Anacardiaceae). Eur Sci J 13(36): 312.
- Begbin KE, Odoh AE, Zougrou N’ge, Kablan Alc, Kouakou Kk (2021) Evaluation of the hypoglycemic and antihyperglycemic activities of the aqueous extract of the leaves of cnestis ferruginea vahl ex dc. (connaraceae) in healthy mice.
QUICK LINKS
- SUBMIT MANUSCRIPT
- RECOMMEND THE JOURNAL
-
SUBSCRIBE FOR ALERTS
RELATED JOURNALS
- Journal of Blood Transfusions and Diseases (ISSN:2641-4023)
- International Journal of Radiography Imaging & Radiation Therapy (ISSN:2642-0392)
- Journal of Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis Research (ISSN: 2643-0541)
- International Journal of Diabetes (ISSN: 2644-3031)
- International Journal of Medical and Clinical Imaging (ISSN:2573-1084)
- Chemotherapy Research Journal (ISSN:2642-0236)
- Journal of Oral Health and Dentistry (ISSN: 2638-499X)



