Research Article
MHC Genes in Immunized Sea Star Asterias Rubens
3262
Views & Citations2262
Likes & Shares
We recapitulate first, MHC genes from Class I and Class II exist in Echinodermata (Invertebrates), second new genes: HLA-A (Class I), HLADQA1 (Class II) are present in another Echinodermata: the sea star Asterias rubens genome.
INTRODUCTION
MHC genes (Class I, Class II) were discovered, for the first time, in Invertebrates, and particularly in 2 classes of Echinodermata: the ophuirids and the crinoïds out of 5 classes [1]. They show mainly HLAE gene, HLA B gene from MHC Class I [1] and HLADRB1 gene, HLADQB1 gene from MHC Class II.
We attempt in the present work to determine new MHC genes from Class I and Class II in sea star immunized to HRP (Horse- radish Peroxydase) genome.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
Sea stars Asterias rubens were immunized twice to HRP: 100µg/injection in coelomic cavity. 5 days after the last injection, digestive coeca were removed and treated with Trizol (Invitrogen) to obtain RNA.
Genomic Studies: Secondly, cDNA was normalized using double strand specific nuclease essentially as described by Zhulidov [2]. cDNA was fragmented using DNA Fragmentase (New England Biolabs), according to the manufacturer's instructions. After ligation of adapters for Illumina's GSII sequencing system, the cDNA was sequenced on the Illumina GSII platform sequencing 100 bp from one side of the approximately 200 bp fragments. Sequences were assembled using Velvet Zerbino [3]. Assembled nodes were used for further assembly including Beta vulgaris EST-Data from NCBI in MIRA.
RESULTS
An HLA-A MHC gene from Class I is found with a significant e-value. The sequence of the transcriptome appears in 5’-3’:
5’CCACAGACAAGATCATACTGAATGAGCAAAAACTGGAAGCATTCCCTTTGAAAACTGGCACAAGACAGGGATGCCCTCTCTCACCACTCCTATTCAACATAGTGTTGGAAGTTCTGGCCAGGGCAATCAGGCAGGAGAAGGAAATAAAGGT 3’
At last, a HLADQA1 MHC gene from Class II is described by mapping [4]: it is shown in Figure 1.
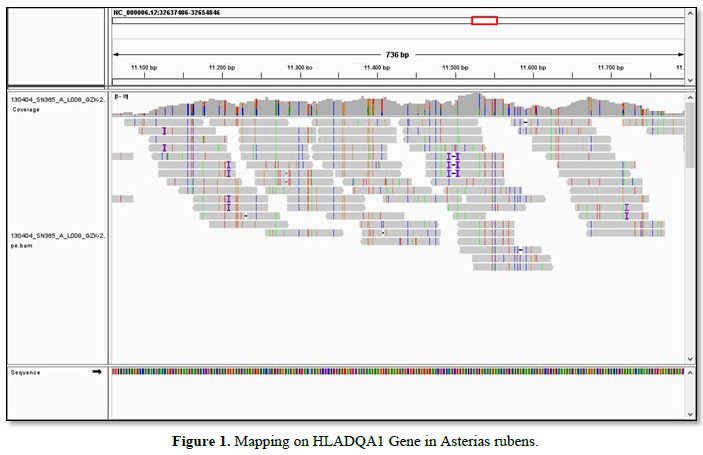
CONCLUSION
Two new MHC genes (1 from Class I, the other one from Class II) are described in this work to summarize the results: HLA-A and HLADQA1. They complete in a positive way our study in various classes of Echinodermata such as: Ophiocomina nigra (Ophuirids), Antedon bifida (Crinoïds), Asterias rubens (Asterids).
However, we suppose that the 2 other classes of Echinodermata (Holothurids and Echinids) have not MHC genes. Further studies are nevertheless necessary to confirm this hypothesis.
- Leclerc M (2020) Evidence of MHC Class I and Class II Genes in Echinodermata. Proteomics Bioinformatics 2(1): 59-61.
- Zhulidov PA, Bogdanova EA, Shcheglov AS, Vagner LL, Khaspekov GL, et al. (2004) Simple cDNA normalization using kamchatka crab duplex‐specific nuclease. Nucleic Acid Res 3: 32-37.
- Zerbino DR, Birney E (2007) Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res 18: 821-829.
- Leclerc M, Baerlocher L (2021) Mapping on Sea-Star MHC Genes in Invertebrates. Eur J Biol Biotechnol 2(2): 60-62.



