Research Article
Knowledge, Attitude and Barriers of Online Mode of Learning Among B.Sc. Nursing Students, in Selected Nursing College of Madurai District
7932
Views & Citations6932
Likes & Shares
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic has affected the educational system worldwide. Many schools, colleges and universities have temporarily closed in an attempt to reduce the spread of COVID-19. This pandemic shed light on numerous issues affecting classroom learning. Nowadays, teaching and learning has started online. The shift of traditional classroom and face-to-face instructor training to computer-based learning in a virtual classroom makes learning experience entirely different for students. Self-motivation is an essential requirement in online learning. Students need to find motivate them to follow the new educational trends and also equip themselves for future challenges in their education and career.
Objectives: The objectives of the study were, to assess the knowledge and attitude regarding online mode of learning among B.Sc. nursing students, to find out the barrier of online mode of learning among B.Sc. nursing students, and to find out the association between the knowledge and attitude score with demographic variables.
Methods: A descriptive online survey approach was used for conducting the study. Study was conducted among 50 nursing students from a selected nursing college in Madurai. Data was collected by using structured knowledge questionnaire to assess knowledge regarding online mode of learning, Rating scale was used to assess attitude and opinion questionnaire to identify the barriers in regarding online mode of learning.
Results: Majority of the nursing students (43) 86% had good knowledge, (4) 8% had excellent knowledge (3) 6% had average knowledge regarding online mode of learning. With regard to attitude, (22) 44% had neural attitude and (28) 56% had favorable attitude towards online mode of learning. There is no significant association between knowledge except age in years (chi square=26.96) and gender (chi-square value=7.20) with demographic data of the samples (p<0.05). There is no significant association between attitude except for the need for online mode of learning (chi square=4.468) with demographic data of the samples (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Online learning is a boon to the students of the present generation. However, at its initial stage, it may pose certain threats to the students. An Attitude change and technological literacy would help them to gain confidence in order to succeed in the learning activity with positive vibration.
Keywords: Online mode of learning, Knowledge, Attitude, Barriers, Nursing students
INTRODUCTION
The current education system in India is based only on traditional approach of learning, that is, they follow the conventional face-to-face lectures in the class room. The unexpected outbreak of a deadly disease called COVID-19 caused by a Corona Virus (SARS-CoV-2) shook the whole world [1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced COVID-19 as a pandemic, that has posed a current threat to humanity. This has imposed a global shutdown of several activities, including educational activities and this has emanated in tremendous crisis [2]. So, the educational institutions have switched on to online mode of learning to cater to the needs of the students.
Online learning endows an opportunity to have live applications, such as Word and PowerPoint. Learner can use programs autonomously to do tasks and assignments. This online learning environment is more effective and helps the Students to learn the subject matter clearly [3]. A qualitative
Online learning endows an opportunity to have live applications, such as Word and PowerPoint. Learner can use programs autonomously to do tasks and assignments. This online learning environment is more effective and helps the Students to learn the subject matter clearly [3]. A qualitative
study was conducted on the experiences of nursing students during the abrupt change from face-to-face to e-learning during the first month of confinement due to COVID-19 in spin. An induction thematic analysis was conducted among 32 students. The following themes like, practicing care, uncertainty, time, teaching methodologies, context of confinement and difficulties and face to face teaching were analyzed. The finding of the study shown that, living in a rural environment with limited electronic resources brings more limitation on e-learning. Online teaching has substituted the traditional lecture-based teaching method. However, clinical practices are more essential for the training of the student nurses [4]. This study will help to understand the actual problem faced by the students while conducting online classes, solve the problem and make the education system more effective.
OBJECTIVES
- To assess the knowledge and attitude regarding online mode of learning among Sc. nursing students.
- To find out the barrier of online mode of learning among Sc. nursing students.
- To find out the association between the knowledge and attitude score with demographic
METHODS AND MATERIALS
A descriptive online survey design was used to conduct the study. Study was conducted among 50 II-year B.Sc. nursing students from a selected nursing college in Madurai district. Purposive sampling was used to select the subjects. The instruments used were developed by the researcher. The researcher used the following instrument for collecting the data.
Tool 1
A descriptive online survey design was used to conduct the study. Study was conducted among 50 II-year B.Sc. nursing students from a selected nursing college in Madurai district. Purposive sampling was used to select the subjects. The instruments used were developed by the researcher. The researcher used the following instrument for collecting the data.
Tool 1
Demographic Performa was used to collect information regarding the characteristics of the participants. The items included in the tool were age in years, gender, previous knowledge on online mode of learning, are you using online mode for learning purpose, frequency of using online mode, need for learning nursing subjects, need for using online mode, the modes of online class room you know, availability of gadgets, and which gadgets frequently used for learning purpose.
Section A
Section A
Included structured knowledge questionnaire regarding online mode of learning. This multiple-choice questionnaire consisted of 10 items which included methods of online mode of learning and its usage with four options. Correct response carried one mark and wrong response carried zero mark. Knowledge Scores was interpreted as excellent (more than 7), good (4-6) and average (less than 3).
Section B
Rating scale to assess attitude towards online mode of learning was used. These 5 points like rt scale consisted of 10 statements on online mode of learning. Total score was 1 to 50. Attitude score was divided as favorable (33-50), neutral attitude (16-32) and unfavorable attitude (1-15).
Tool was submitted to experts from the fields of nursing, computer literacy and statistician. The experts were requested to give for their opinion regarding the relevancy and appropriateness. Modifications were done based on expert’s suggestions. The reliability of knowledge questionnaire was assessed by split half method. The reliability of the tool was r=0.80 which was reliable. Cronbach’s alpha was used to determine the attitude scale reliability, r=0.8 was found reliable.
Procedure for Data Collection
Procedure for Data Collection
Prior to data collection, permission was obtained from the Principal of Sacred Heart Nursing College. The written informed consent was obtained from the subjects before data collection. Purpose of the study was explained to the subjects. After collecting the participant’s information, structured knowledge questionnaire, rating scale and opinion questionnaire on barriers of online mode of learning were given to the subjects to collect the information.
RESULTS
RESULTS
Descriptive statistics was used to find out the frequency and percentage for demographic data. Chi-square test was used to determine the association between knowledge and attitude score on online mode of learning with selected demographic variables.
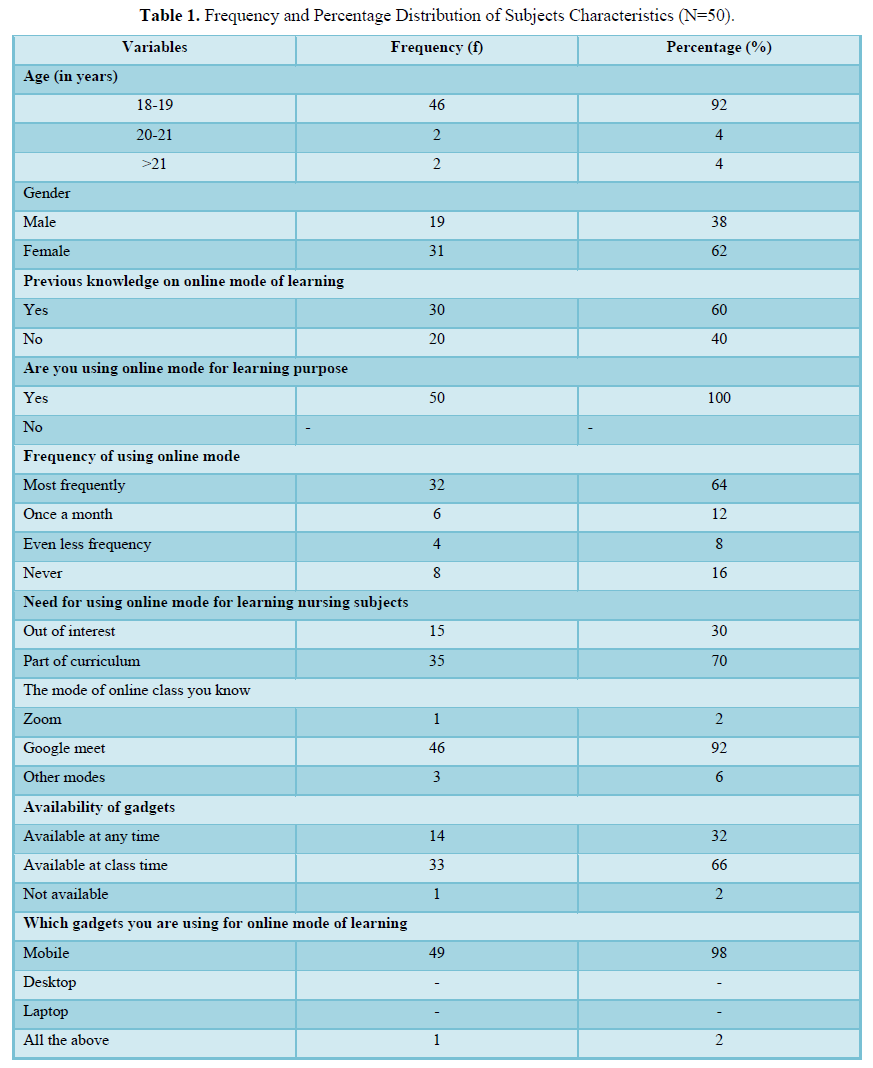
With regard to age in years, majority of (46) 92% belong to 18-19 years. Most of the (31) 62% were females. Majority i.e. (30) 60% had previous knowledge on online mode of learning. Data showed that majority of the subjects were using online mode for learning purpose i.e. (50)100% and 32(64%) had frequently been utilizing online mode for learning nursing subjects, most of participants’ i.e. (35) 70% had need for learning nursing subjects as part of curriculum. Majority i.e. (46)92% participants liked to use Google meet online mode. Students who participated in the study were (49)98% having mobile gadgets for online mode of learning and majority of the participant’s i.e. (33)66% had availability of gadgets at class time (Table 1).
DISTRIBUTION OF SUBJECTS BASED ON KNOWLEDGE REGARDING ONLINE MODE OF LEARNING
DISTRIBUTION OF SUBJECTS BASED ON KNOWLEDGE REGARDING ONLINE MODE OF LEARNING
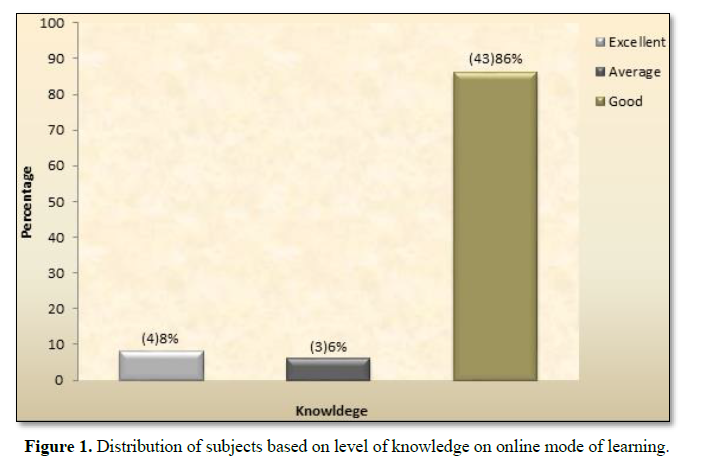
Figure 1 presents that majority (43)86% of the nursing students had good knowledge on online mode of learning and (4)8% excellent knowledge and (3)6% had average knowledge.
DISTRIBUTION OF SUBJECTS BASED ON ATTITUDE TOWARDS ONLINE MODE OF LEARNING
Figure 2 presents that (22) 44% and (28) 56% have neutral and favorable attitude towards online mode of learning respectively.
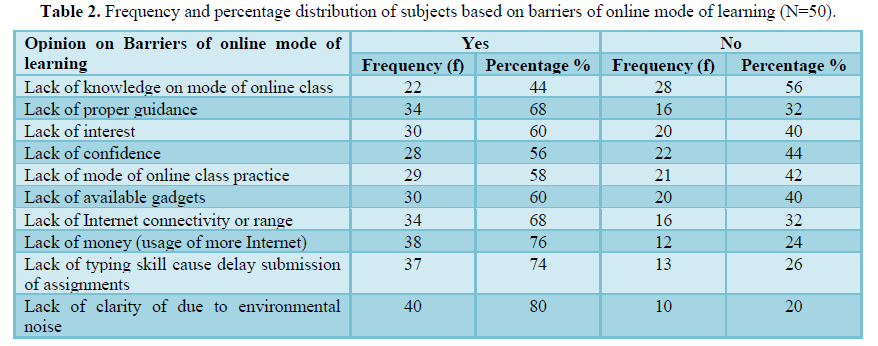
The data represented in Table 2 shows that, lack of knowledge on online mode of learning (22) 44% were stated yes. And (28) 56% were stated no. with regard to lack of proper guidance (34) 68% expressed yes and (16) 32% were expressed no. with regard to lack of interest majority (30) 60% were supported yes and only(20) 40% were expressed no. with regard to lack of confidence most of them (28) 56% were pointed yes and (22) 44% stated no. with regard to lack of mode of online class practice (29) 58% expressed yes and(21) 42% were no. with regard to lack of available gadgets(30) 60% and (20) 40% were stated yes and no respectively.
With regard to Lack of Internet connectivity most of the samples (34) 68% were pointed yes and (16) 32% expressed no. With regard to lack of money (usage of more Internet) most of the subjects were expressed yes (38) 76%, and (12) 24%-pointed no. with regard to lack of typing skill cause delay submission of assignments (37) 74% were stated yes and (13) 26% stated no. with regard to lack of clarity due to environmental noise most of them (40) 80% were pointed yes and (10) 20% expressed no.

ASSOCIATION BETWEEN KNOWLEDGE SCORE WITH DEMOGRAPHIC VARIABLES
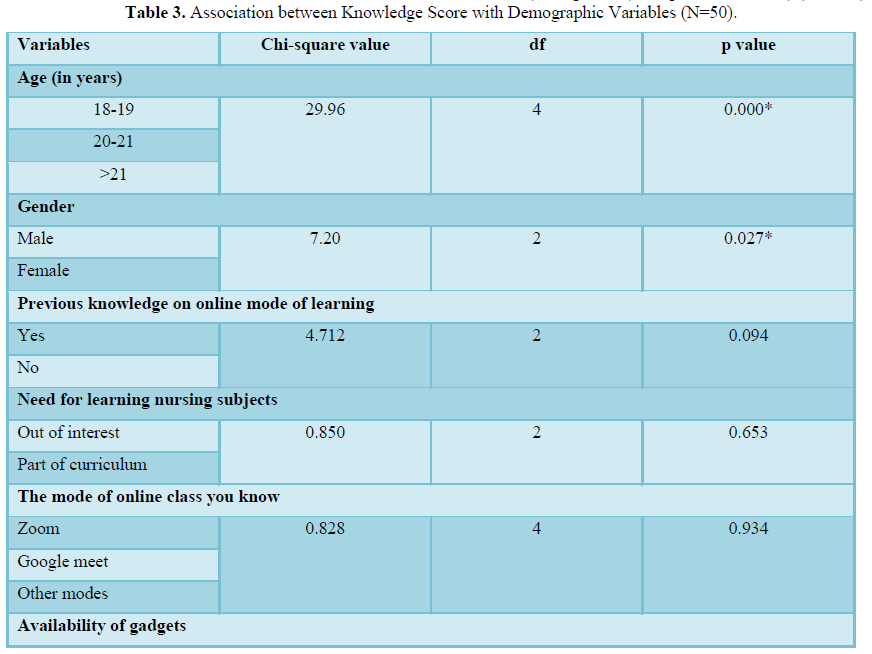
There was no statistical association between knowledge score with selected demographic variables such as, previous knowledge on online mode of learning, need for learning nursing subjects, the mode of online class you know, availability of gadgets and which gadgets you are using for online mode of learning except age in years (chi-square value=26.96) and gender (chi-square value=7.20) (Table 3).
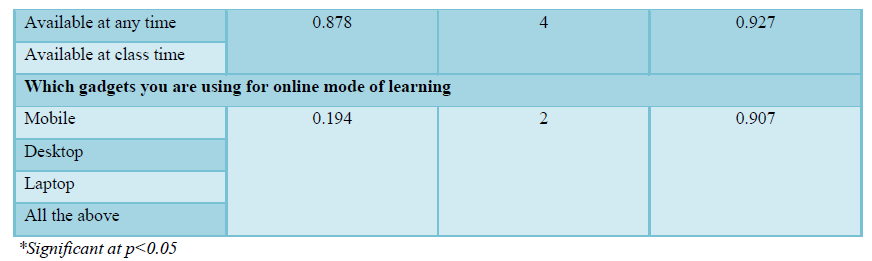
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN LEVELS OF ATTITUDE TOWARDS ONLINE MODE OF LEARNING WITH SELECTED DEMOGRAPHIC VARIABLES


ASSOCIATION BETWEEN LEVELS OF ATTITUDE TOWARDS ONLINE MODE OF LEARNING WITH SELECTED DEMOGRAPHIC VARIABLES
There was no statistical association between levels of attitude with demographic variables except need for online mode of learning (chi square=4.468) (Table 4).
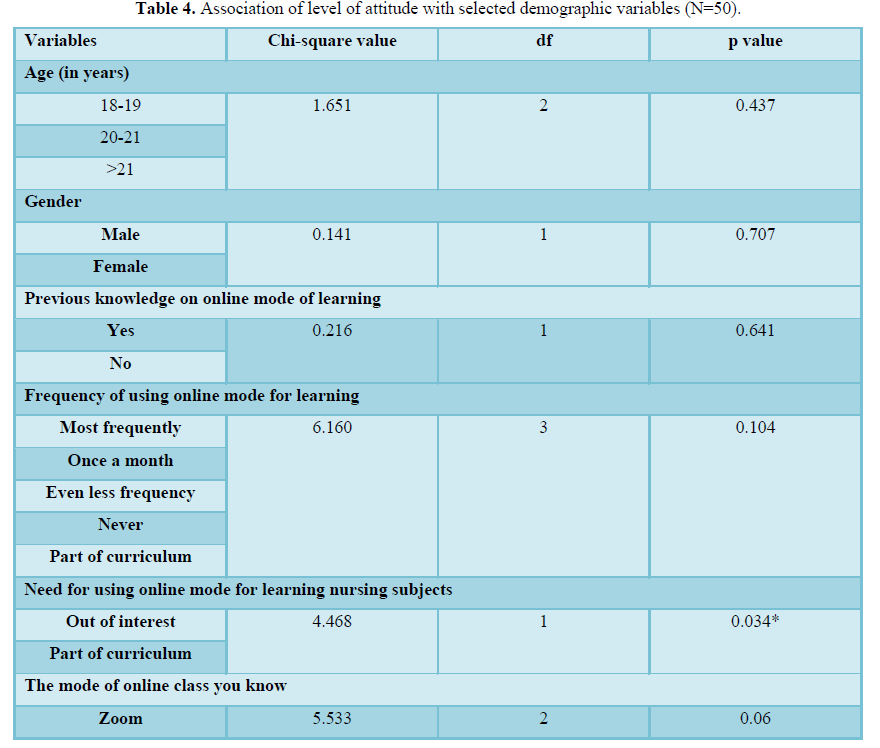
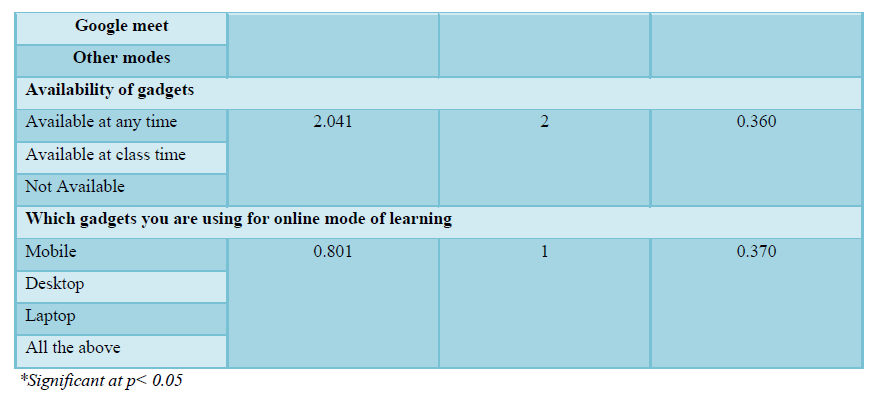
DISCUSSION
Due to the current pandemic situation, Institutional education activities have become online. Online learning platforms are contributing free access to learning [2]. There are many benefits observed in e-learning such as improvement learning outcome, proper utilization of the learning materials and reduction of failure [5].
The present study findings show that, the majority of the subjects (43) 86% had good knowledge and (3) 6% had average knowledge and (4) 8% had excellent knowledge on online mode of learning. In a study conducted by Mahmoodi, Maleki, Sanisales among nursing students showed 4.32 points reported improvement observed in learning process and 4.67 points increases in their creativity. With regard to attitude, majority (22) 44% had neutral attitude, (28) 56% had favorable attitude towards online mode of learning. And there is no statistical association with knowledge score except age in years (chi square=26.96); and gender (chi-square value=7.20) with demographic variables. And also, there is no statistical association with attitude score except need for online mode of learning (chi square=4.468) with demographic variables. A systemic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCT) was conducted among 2491 nurses and nursing students to assess the impact of e-learning on nurses and nursing student’s knowledge, skill and satisfaction. Cochrane reviews extraction was used for tool development. The study result revealed that little improvement associated with e- learning compared to face-to-face method on knowledge and skill. However, there is no statistical significance (P=0.39, MD 0.44, 95% CI-0.57 to1.46) and (P=0.13, MD 0.03, 95% CI-0.09 to 0.69) Knowledge and skill respectively [6].
In the present study, 68% college students expressed issues due to internet connectivity and 76% of have pointed usage of net pack. A similar descriptive cross sectional online survey was conducted among nursing students and teachers of Nepal to assess the impact of e-learning during COVID- 19 Pandemic. The study results revealed that, the teachers expressed 42.3% got disturbed online class due to electricity problem and 48.1% due to internet issues. Majority 64.4% of the students pointed that, they problem in internet access for online class, 64.3% used net pack, and 58.4 % used mobile phone for online class. The research study concludes that e- learning is a wonderful opportunity to continued education, but there are some problems faced by teachers and students [7].
CONCLUSION
Switching from traditional classroom into e-learning brings a new learning experience for a nursing student. The student with a traditional mind set it is very difficult to adapt this online learning environment. However, they need to accept the new learning circumstances with the open mind and heart. And also, they should equip themselves for this new learning environment for the successful completion of their course. Self-motivation and positive attitude were essential components for the online learning. Positive attitude with technological literacy would help them to gain confidence and lead them to accomplish their learning task.
Based on the study findings, it was presumed that structured enlightenment program was effective in improving knowledge and imbibing more favorable attitude on online mode of learning among college students. It is recommended to conduct qualitative studies to explore the factors affecting the online mode of learning. Nurse educator should provide opportunity to improve the clinical skill for providing patient care. This study will help to solve the actual problem faced by student nurses while attending online classes and bring the better education system in the world.
LIMITATIONS
LIMITATIONS
The study is limited to nursing students studying in selected nursing college of Madurai. The descriptive data regarding knowledge and attitude and opinion towards barriers of online mode of learning was collected. The study finding was limited to small sample size.
- Dhawan S (2020) Online learning: A panacea in the time of COVID-19 J Educ Technol Syst 49(1): 5-22.
- Adedoyin OB, Soykan E (2020) COVID-19 pandemic and online: Challenges and opportunities. Interact Learn Environ pp: 1-14.
- Muntajeeb AB (2011) A Critical Study of Effectiveness of Online Learning on student’s achievement. i-managers J Educ Technol 7(4): 28-34.
- Ramos-Morcillo AJ, Costa LC, Moral-Garcia JE, Martinez MR (2020) Experiences of Nursing Students during abrupt change from face -to- face to e- Learning education during first Month of Confinement due to COVID-19 in Int J Environ Res Public Health 5519: 1-15.
- Riffell S, Sibley D (2005) Using web-based instruction to improve large undergraduate biology courses: An evaluation of a hybrid course Comput Educ 44(3): 217-235.
- Lahti M, Hatonen H, Valimaki M (2014) Impact of e- learning on nurses' and student nurse’s knowledge, skills, and satisfaction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Nurs Stud 51(1): 136-149.
- Subedi S, Nayaju S, Subedi S, Shah SK, Shah JM (2020) Impact of e-learning during COVID-19 Pandemic among nursing students and teachers of Nepal. Int J Sci Health Care Res 5(3): 68-75.
QUICK LINKS
- SUBMIT MANUSCRIPT
- RECOMMEND THE JOURNAL
-
SUBSCRIBE FOR ALERTS
RELATED JOURNALS
- BioMed Research Journal (ISSN:2578-8892)
- International Journal of Radiography Imaging & Radiation Therapy (ISSN:2642-0392)
- Advance Research on Alzheimers and Parkinsons Disease
- Advance Research on Endocrinology and Metabolism (ISSN: 2689-8209)
- Journal of Blood Transfusions and Diseases (ISSN:2641-4023)
- Journal of Neurosurgery Imaging and Techniques (ISSN:2473-1943)
- Journal of Ageing and Restorative Medicine (ISSN:2637-7403)




