667
Views & Citations10
Likes & Shares
The study was conducted with 13 eggplant lines/variety at the farm of
Olericulture Division, HRC, Bangladesh Agricultural Research Institute, Gazipur
during the summer season of 2017 to develop new high yielding OP variety having
tolerance to high temperature, high humidity, eggplant fruit and shoot borer,
bacterial wilt and phomopsis blight. The lines varied significantly for their
response to all characters (P<0.05). The line SM286A required minimum 90.67
days to first harvest. Maximum marketable fruit number was obtained by SM323
(41.56). Heavy sized fruit was harvested by SM328 (111.84 g), which was
statistically similar with SM275 (107.33 g), SM236A (97.00 g). The range of
fruit infection by BFSB was 12.56-23.33%, while lowest in SM236A (12.56%). In
case of bacterial wilt (BW) infestation at field level performance, zero
percent incidences was observed in SM232, SM236A, SM286A, SM328. The yield range
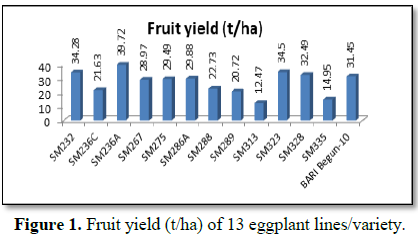
of eggplant lines was 12.47-39.72 t/ha. The highest fruit yield was recorded
from the line SM236A (39.72 t/ha), which was followed by SM323 (34.50 t/ha),
SM232 (34.28 t/ha), SM328 (32.49 t/ha), BARI Begun-10 (31.45 t/ha), SM286A
(29.88 t/ha), SM275 (29.49 c t/ha) and lower yield were recorded from SM313
(12.47 t/ha). Considering earliness, tolerance to fruit infection by BFSB,
bacterial wilt infestation, phomopsis blight infestation, attractive fruit
shape and fruit color, last of all fruit yield, the lines SM232, SM275, SM288,
SM323, SM328 were found promising. So these five lines can be selected for
further confirmation.
Keywords: Eggplant, Yield,
Insect and diseases, Summer, Bangladesh
INTRODUCTION
Brinjal or eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) is an important Solanaceous crop of sub
tropics and tropics. The name brinjal is popular in Indo-Bangla subcontinents
and is derived from Arabic and Sanskrit whereas the name eggplant has been
derived from the shape of the fruit of some varieties, which are white and
resemble in shape to chicken eggs. It is also called Aubergine (French word) in
Europe. The eggplant is of much importance in the warm areas of Far East, being
grown extensively in India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, China and the Philippines. It
is also popular in Egypt, France, Italy and United States. In Bangladesh, India
it is one of the most common, popular and principal vegetable crops grown
throughout the country. It is a versatile crop adapted to different
agro-climatic regions and can be grown throughout the year.
Eggplant is rich in calories, protein,
carbohydrate, fiber, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, flavonoids, etc. One cup
of cooked eggplant, weighing around 99 grams (g) contains: 35 calories, 0.82 g
of protein, 8.64 g of carbohydrate, of which 3.17 g is sugars, 0.23 g of fat,
2.5 g of dietary fiber, 188 mg of potassium, 6 mg of calcium, 1 mg of sodium,
0.12 mg of zinc, 1.3 mg of vitamin C, 0.25 mg of iron, 11 mg of magnesium, 15
mg of phosphorus, 14 micrograms (mcg) of folate, 85 mcg of vitamin B6, 2.9 mcg
of vitamin K. Eggplants also contain flavonoids, such as anthocyanins.
Anthocyanins are water-soluble pigments that have many health benefits. The
skin of the eggplant is rich in antioxidants, fiber, potassium and magnesium.
The fiber, potassium, vitamin C, vitamin B6 and phytonutrient content in
eggplants all support heart health. Certain flavonoids, including anthocyanins,
may be associated with a lower risk of mortality from heart disease [1].
Anthocyanins and chlorogenic acid has been shown to decrease low-density lipid (LDL) levels as well also acts as an
antimicrobial, antiviral and anti-carcinogenic agent and anti-cancer effects. Anthocyanin
in the eggplant skin is a powerful antioxidant
Eggplant is the most popular vegetable crop in respect of total acreage
(50,415 ha) and production (5,04,817 t) in Bangladesh with an average yield of
10.0 t/ha [2], which is very low as compared to that in other tropical
countries. This low yield may be due to lack of high yielding varieties with
pest resistance. High yielding variety is an important factor for maximizing
the yield of eggplant.
A number of cultivars are grown in Bangladesh, consumer preference
being dependent upon fruit color, size and shape. We are accustomed to purple
eggplant, but in addition to purple eggplant, there is also green eggplant.
There is a great chance to get higher yield by collecting new germplasm of eggplant.
With this information in mind, Olericulture division collected a lot of
eggplant germplasm and evaluated last year and selected 12 eggplant lines. This
study was undertaken to study the performance of these lines regarding yield
having tolerance to high temperature, high humidity, eggplant fruit and shoot
borer, bacterial wilt and phomopsis blight [3].
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The experiment was conducted at the experimental farm of Joydebpur
during the summer of 2017. The experimental field was at 23.9917°N Latitude and
90.4124°E Longitudes having an elevation of 8.2 m from sea level. Thirteen
eggplant lines/varieties viz., SM232, SM236C, SM236A, SM267, SM275, SM286A,
SM288, SM289, SM313, SM323, SM328, SM335, BARI Begun-10 included in the study.
The seeds were sown on the seedbed on 15 March 2017. Thirty two days old
seedlings were transplanted in the main field on 16 April, 2017. The experiment
was laid out in a RCB design with three replications. The unit plot size was
7.5 × 0.70 m and 10 plants were accommodated in a plot with a plant spacing of
75 cm apart in single row maintaining a row to row distance of 1 m with 50 cm
drain. The land was fertilized with cow dung, N, P, K, S, Zn and B @ 10,000
100, 30, 75, 13, 1.5 and 0.8 kg/ha, respectively. One third of the cow dung and
half of P and full of S, Zn and B were applied during final land preparation.
Rest of cow-dung and P and 1/3 of K were applied as basal in pit. Entire amount
of N and rest of K were applied in four equal installment starting from 20 days
after transplanting. Rest three installments were applied at vegetative,
flowering and initial fruiting stage. Irrigation, weeding, crop protection
measures and other intercultural operations were done following standard
practice. Data on days to 1st harvest, marketable fruit number/plant, average
fruit weight (g), fruit weight/plant (kg), fruit length (cm), fruit diameter
(cm), plant height at 1st harvest (cm), plant height at last harvest
(cm), fruit infection by BFSB (%), bacterial wilt infestation (%), little leaf
infestation (%), phomopsis blight infestation (%), fruit yield (t/ha), fruit
shape and fruit color were recorded from five randomly selected plants per
entry per replication. The information on different characters was
statistically analyzed.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Mean performances of eggplant lines/varieties are presented in Tables 1 and 2 and Figure 1. The lines varied significantly for their response to days
to 1st harvest, marketable fruit number/plant, average fruit weight,
fruit weight/plant, fruit length, fruit diameter, plant height at 1st
harvest, plant height at last harvest, fruit infection by BFSB, bacterial wilt
infestation, fruit yield (P<0.05). In respect of days to first harvest, the
earliest line was SM286A (90.67 days) which was statistically similar with
SM323 (91.59 days), SM236A 91.67 days), SM232 (92.00 days) and SM313were the
most delayed (109.67 days). The range of marketable fruit number was
(15.67-41.56). The highest marketable fruit number per plant was counted in SM323
(41.56) which was statistically similar with SM236A (37.67), SM286A (36.67),
while lowest fruit number was counted in SM313 (15.67). Average fruit weight is
an important criterion to select a high yielder line. The heaviest fruit was
produced in SM328 (111.84 g), which was statistically similar with SM275
(107.33 g), SM236A (97.00 g), while lightest fruit was in SM313 (73.33 g).
Fruit weight/plant was maximum in SM236A (3.61 kg) which was followed bySM323
(3.14 kg), SM232 (3.12 kg), SM328 (2.95 kg), while minimum was in SM313 (1.13
kg). The longest identical fruit was produced by BARI Begun-10 (25.12 cm) which
was followed by SM288 (20.33 cm) and SM328 produced the shortest fruit (9.45
cm). The higher diameter fruit was produced by the line SM335 (9.23 cm)
followed by SM328 (8.93 cm) and minimum was by SM323 (3.40 cm). The range of
plant height at first and last harvest was 55.00-80.67 days and 91.00-126.58
days, respectively. The range of fruit infection by BFSB was 12.56-23.33%,
while lowest in SM236A (12.56 %), which was statistically similar with SM328
(12.67%), SM286A (14.00%), SM323 (14.56%), SM232 (15.00%) and highest was in
SM288 (23.33%). In case of bacterial wilt (BW) infestation at field level
performance, zero percent incidence was observed in SM232, SM236A, SM286A,
SM328, while maximum was observed in SM335 (15.59%). Zero percent phomopsis
blight diseases incidence was observed in SM232, SM236A, SM288 while maximum
was observed in SM335 (10.00 %). Morphological characteristics of the lines are
presented in Table 2.
Four types of fruit shape was observed among the lines viz., oblong (5
lines), cylindrical (3 lines/variety), elongate (3 lines), round (2 line),
while in term of fruit color, all the lines were purple colored except 2 lines
were green colored (SM286A, SM289).
CONCLUSION
Though the lines SM236A, SM323, SM232, SM328, SM286A were high yielder,
but considering earliness, tolerance to fruit infection by BFSB, bacterial wilt
infestation, phomopsis blight infestation, attractive fruit shape and fruit
color, last of all fruit yield, the lines SM232, SM275, SM288, SM323, SM328
were found promising. So these five lines can be selected for further
confirmation [4].
1. Streppel MT, Ocke´ MC, Boshuizen HC, Kok FJ,
Kromhout D (200) Dietary fiber intake in relation to coronary heart disease and
all-cause mortality over 40 years: The Zutphen study. Am J Clin Nutr 88:
1119-1125.
2. (2017) Year Book of Agricultural Statistics
of Bangladesh 2016. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, Ministry of Planning,
Government of Peoples Republic of Bangladesh, Dhaka, Bangladesh, pp: 249-290.
3. https://www.Eggplant-health-benefits-and-tasty-tips
4.
https://www.THealth
QUICK LINKS
- SUBMIT MANUSCRIPT
- RECOMMEND THE JOURNAL
-
SUBSCRIBE FOR ALERTS
RELATED JOURNALS
- Journal of Veterinary and Marine Sciences (ISSN: 2689-7830)
- Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine (ISSN:2641-6948)
- Journal of Genetics and Cell Biology (ISSN:2639-3360)
- Proteomics and Bioinformatics (ISSN:2641-7561)
- Food and Nutrition-Current Research (ISSN:2638-1095)
- Journal of Womens Health and Safety Research (ISSN:2577-1388)
- Journal of Astronomy and Space Research